CBSE Class 10 Science How Do Organisms Reproduce VBQs read and download in pdf. Value Based Questions come in exams for Science in Class 10 and are easy to learn and helpful in scoring good marks. You can refer to more chapter wise VBQs for Class 10 Science and also get latest topic wise very useful study material as per latest NCERT book for Class 10 Science and all other subjects for free on Studiestoday designed as per latest Class 10 CBSE, NCERT and KVS syllabus and examination pattern
VBQ for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 How do the Organisms Reproduce
Class 10 Science students should refer to the following value based questions with answers for Chapter 8 How do the Organisms Reproduce in Class 10. These VBQ questions with answers for Class 10 Science will come in exams and help you to score good marks
Chapter 8 How do the Organisms Reproduce VBQ Questions Class 10 Science with Answers
MCQ Questions for NCERT Class 10 Science How do the Organisms Reproduce
Question. Choose the right option.
Answer : C
Question. Identify the organism
(a) Rhizobium
(b) Rhizopus
(c) Rhizoid
(d) Mushroom
Answer : B
Question. Chose the correct option
Answer : B
Question. The type of reproduction taking place is
(a) Budding
(b) Fragmentation
(c) Regeneration
(d) Fission
Answer : C
Question. Identify the type of cell division taking place
(a) Longitudinal cell division taking place
(b) Transversal cell division in Paramecium
(c) Longitudinal cell division in Paramecium
(d) Transversal cell division in Amoeba
Answer : B
Question.
Answer : A
Question. Union of male and female gametes forms
(a) Egg
(b) Embryo
(c) Zygote
(d) Spore
Answer : C
Question. Which of the following is a contraceptive?
(a) Copper-T
(b) Condom
(c) Diaphragm
(d) All of these
Answer : B
Question. Spirogyra reproduces by
(a) Fission
(b) Regeneration
(c) Fragmentation
(d) Budding
Answer : C
Question. The process where the unfertilised egg is released out of the body with the blood used to nourish the embryo is known as
(a) Menstruation
(b) Fertilisation
(c) Germination
(d) Pollination
Answer : A
Question. IUCD is for
(a) Vegetative propagation
(b) Contraception
(c) Increasing fertility
(d) Avoiding miscarriage
Answer : B
Question. After fertilisation name the part which develops into the seeds
(a) Ovary
(b) Ovule
(c) Pollen grain
(d) None of the above
Answer : B
Question. What are the functions performed by the testis in human males?
(a) Production of gametes–eggs and secretion of sex hormones–estrogen
(b) Production of gametes–sperms and secretion of sex hormones–testosterone
(c) Production of gametes–sperms and secretion of sex hormones–estrogen
(d) None of the above
Answer : B
Question. The process in which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell is divided to form two daughter cells is known as?
(a) Karyokinesis
(b) Cytokinesis
(c) Meiosis
(d) Mitosis
Answer : D
Question. The common passage meant for transporting urine and sperms in males is
(a) Ureter
(b) Vas deferens
(c) Urethra
(d) Anus
Answer : A
Question. Vegetative propagation in potato takes place through
(a) Stem
(b) Root
(c) Leaves
(d) Seeds
Answer : A
Question. The anther contains
(a) Sepals
(b) Ovules
(c) Carpel
(d) Pollen grains
Answer : D
Question. Unisexual flowers contain
(a) Both stamen and carpel
(b) Only stamen
(c) Only carpel
(d) Either stamen or carpel
Answer : D
Question. The full form of AIDS is
(a) Acquired Immune Deficiency System
(b) Acquired Immune Disease Syndrome
(c) Acquired Immediate Deficiency Syndrome
(d) Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrome
Answer : D
Question. The number of chromosomes in human ovum is
(a) 21
(b) 22
(c) 23
(d) 24
Answer : C
Question. Pollen grains are produced by
(a) ovary
(b) ovule
(c) apther
(d) corolla
Answer : C
Question. The seed that contains the future plant is called the
(a) cotyledons
(b) seed coat
(c) germ cells
(d) embryo
Answer : D
Question. In a potato, vegetative propagation takes place by:
(a) root
(b) leaf
(c) stem tuber
(d) grafting
Answer : C
Question. Where does fertilisation take place?
(a) Uterus
(b) Vagina
(c) Fallopian tube
(d) Cervix
Answer : C
Question. The flower of the Hibiscus plant is
(a) bisexual
(b) unisexual
(c) neuter
(d) very small
Answer : A
Question. The ability to reproduce is lost in a female after
(a) fertilisation
(b) menstruation
(c) gamete formation
(d) menopause
Answer : D
Question. The embryo in humans gets nutrition from the mother’s blood with the help of a special tissue called
(a) Placenta
(b) Villi
(c) Uterus
(d) Womb
Answer : A
Question. The ability of an organism to develop whole body from a broken piece or fragment is called
(a) binary fission
(b) budding
(c) multiple fission
(d) regeneration
Answer : D
Question. During favourable conditions, Amoeba reproduces by
(a) multiple fission
(b) binary fission
(c) budding
(d) fragmentation
Answer : B
Question. When the foetus is growing inside the uterus it needs nutrients. Which part provides these nutrients?
(a) Placenta
(b) Amniotic sac
(c) Oviduct
(d) Uterus
Answer : A
Question. In Rhizopus, tubular thread like structures bearing sporangia at their tips are called
(a) filaments
(b) hyphae
(c) rhizoids
(d) roots
Answer : B
Question. In the list of organisms given below, those that reproduce by the asexual method are
(i) banana
(ii) dog
(iii) yeast
(iv) Amoeba
(a) (ii) and (iv)
(b) (i), (iii) and (iv)
(c) (i) and (iv)
(d) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
Answer : B
Question. Which is the most common method of reproduction in majority of fungi and bacteria?
(a) Budding
(b) Spore formation
(c) Binary fission
(d) Multiple fission
Answer : B
Question. Plants like banana, rose, jasmine, orange have lost the capacity to produce
(a) seeds
(b) buds
(c) flower
(d) roots
Answer : A
Question. The ability of a cell to divide into several cells during reproduction in Plasmodium is called
(a) budding
(b) multiple fission
(c) binary fission
(d) reduction division
Answer : B
Question. The period of pregnancy is called
(a) gestation period
(b) incubation period
(c) ovulation
(d) menstruation period
Answer : A
Question. What marks the beginning of the reproductive life of a woman?
(a) Menopause
(b) Menarche
(c) Fertilisation
(d) Ovulation
Answer : B
Question. Which of the following is not an artificial method of vegetative propagation?
(a) Cutting
(b) Layering
(c) Budding
(d) Grafting
Answer : C
Question. Along the path of the vas-deferens the secretions of which gland provide nutrition to the sperms?
(a) Prostate glands
(b) Seminal vesicles
(c) Scrotum
(d) Urinary bladder
Answer : B
Question. Vegetatively propagated plants
(a) do not bear roots
(b) do not bear buds
(c) are genetically similar
(d) are genetically dissimilar
Answer : C
Fill in The Blank
Question. Fertilization occurs in the ..........tube.
Answer : Fallopian
Question. Pollen grains are transferred from stamens to ......... of carpel.
Answer : Stigma
Question. In ......... vegetative propagation occurs by leaves.
Answer : Bryophyllum
Question. An egg cell of a plant is contained in an .......... present in an ovary.
Answer : Ovule
Question. Ovulation in female human beings stops after the age of ..........
Answer : 45-50
Question. Transfer of pollen from one flower to stigma of another flower of same species is termed ..........
Answer : Cross-pollination
Question. The gametes are formed in most of the multicellular organisms by a process of cell division called .......... .
Answer : Meiosis
Question. Pollen grains are produced by .........
Answer : Stamens
Question. If the .......... in the male is blocked, sperms can be prevented to ......... the egg.
Answer : Vas deferens, fertilize
Question. Plants raised by vegetative propagation bear early .......... and .......... .
Answer : Flowers, Fruits
Question. Simply break up into smaller pieces upon maturation is found in ..........
Answer : Spirogyra
True/False
Question. Fertilization is the fusion of sperm and ovum.
Answer : True
Question. Reproducing cells don not replicate DNA.
Answer : False
Question. Pjants produced by vegetative propagation are genetically similar to the parent plant.
Answer : True
Question. In male adults testes are located in scrotum to facilitate sperm formation.
Answer : True
Question. Copper-T is a contraceptive device used by women.
Answer : True
Question. Sperms mature at a temperature higher than that of human body.
Answer : False
Question. Birds are oviparous.
Answer : True
Question. The maternal blood supply mixes frequently with the foetal blood supply during the exchange of waste materials and nutrients.
Answer : False
Question. Fertilisation of egg takes place in uterus.
Answer : False
Question. The only function of the testes is to produce sperm.
Answer : False
Question. DNA copying mechanisms creates variations which are useful for ensuring the survival of the species.
Answer : True
Question. Reproduction, unlike other life processes, is not essential to maintain the life of an individual organism.
Answer : True
Question. In Spirogyra, asexual reproduction takes place by fragmentation.
Answer : True
Question. Sertoli cells are involved in testosterone production.
Answer : True
Question. Ovulation occurs in reproductively active females roughly in the middle of menstrual cycle.
Answer : True
Assertion and Reason
DIRECTION : In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
(a) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(b) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true but reason (R) is not the correct explanation of assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true but reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false but reason (R) is true.
(e) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Question. Assertion : In human male, testes are extra-abdominai which are present inside scrotum.
Reason : Scrotum has a relatively lower temperature needed for the production and storage of sperms.
Answer : A
Question. Assertion : Asexual reproduction is also called blastogenesis.
Reason : In asexual reproduction, their is no formation and fusion of gametes.
Answer : B
Question. Assertion : Spores are unicellular bodies.
Reason : The parent body simply breaks up into smaller pieces on maturation.
Answer : C
Question. Assertion : Surgical methods are most effective methods of contraception.
Reason : Surgical method blocks gametes transport and hence prevent fertilisation.
Answer : A
Question. Assertion : Clones are offspring of an organism formed by asexual reproduction.
Reason : Clones have exact copies of DNA as their parent.
Answer : B
Question. Assertion : Pollen grains from the carpel stick to the stigma of stamen.
Reason : The fertilised egg cells grow inside the ovules and become seeds.
Answer : D
Question. Assertion : At puberty, in boys, voice begins to crack and thick hair grows on face.
Reason : At puberty, there is decreased secretion of testosterone in boys.
Answer : C
Question. Assertion : Colonies of yeast multiply in sugar solution.
Reason : Sugar is made of sucrose which provides energy for sustaining all life activities.
Answer : A
Question. Assertion : Plasmodium reproduces by multiple fission.
Reason : Multiple fission is a type of asexual reproduction.
Answer : B
Important Questions for NCERT Class 10 Science How do the Organisms Reproduce
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Why does the lining of uterus become thick and spongy every month?
Answer : To receive and nurture the growing embryo, lining of uterus become thick and spongy.
Question. Name the method by which Plasmodium reproduce under favourable conditions. Is this method sexual or asexual?
Answer : Multiple Fission. Asexual
Question. Name the type of cells which undergo regeneration.
Answer : Regenerative cells can proliferate and make large number of cells.
Question. What are sexually transmitted diseases? Name an STD which damages the immune system of human body.
Answer : a. Diseases that spread through the sexual contact.
b. AIDS
Question. What are those organisms called which bear both sex organs in the same individual. Give one example of such organism.
Answer : Bisexual. For example: earthworm, leech, starfish, hibiscus, mustard.
Question. The process of release of an egg from the ovary is called .
Answer: ovulation
Question. Where is DNA found in a cell?
Answer: DNA is found in the nucleus.
Question. What are the two types of reproduction?
Answer: Sexual and asexual reproduction.
Question. Name the largest cell present in the human body.
Answer: The largest cell present in the human body is ovum.
Question. The development of foetus inside the uterus till birth is called .
Answer: gestation
Question. What is Gestation period?
Answer: The time period from the development of the foetus till birth is called gestation period.
Question. What is adolesence?
Answer: Stage between childhood and adulthood.
Question. What is DNA copying?
Answer: DNA in the cell nucleus is the information source for making proteins and different proteins lead to different body designs. Dining reproduction, similar copy of DNA is generated and the process is called DNA copying.
Question. What happens to a slice of bread kept in a moist dark place?
Answer: Rhizopus fungus will develop.
Question. What is the role of seminal vesicles and the prostate gland?
Answer: (i) Seminal vesicles are a pair of thin-walled muscular elongated sac which secrete fluid for nourishment and smooth transport of sperms.
(ii) Prostate gland also produce fluid which is released in the urethra along with the secretion of seminal vesicles to make transportation of sperms easier and also provides nutrition.
Question. Define implantation with respect to human reproductive system.
Answer: It is the close attachment of embryo to the utemine wall.
Question. What is a bisexual flower? Give one example.
Answer: A bisexual flower is a flower that contains both stamens and carpel. Example: Hibiscus.
Question. The development of foetus inside the uterus till birth is called .
Answer: gestation
Question. Name the hormones responsible for secondary sexual characters in
(i) Girls
(ii) Boys.
Answer: (i) Girls: Estrogen and progesterone
(ii) Boys: Testosterone
Question. Define Zygote.
Answer: The cell which is formed by the fusion of a male gamete and a female gamete is called zygote, i.e., it is a ‘fertilised ovum’ or ‘fertilised egg’.
Question. What is the effect of DNA copying which is not perfectly accurate on the reproduction process?
Answer: DNA copying is not perfectly accurate and the resultant errors are a source of variations in populations of organisms.
Question. Name the liqiud which contains sperms.
Answer: Semen.
Question. Why is sexual reproduction considered to be superior to asexual reproduction is terms of evolution?
Answer : Sexual mode of reproduction is a source of variation (in a population of organisms) which ensures survival of the species.
Question. Malarial parasite divides into many daughter individuals simultaneously through multiple fission. State an advantage the parasite gets because of this type of reproduction.
Answer : a. Progeny is identical like parent and in large number.
b. Single individual can reproduce.
Question. Name two simple organisms having the ability of regeneration.
Answer : Planaria/hydra/earthworm.
Question. Give two differences between a male and a female gamete.
Answer : a. Male gamete is smaller in size or compared to the female gamete.
b. Male gamete is motile whereas female gamete is non-motile.
Question. What kind of contraceptive methods prevents STDs and how?
Answer : Barrier method prevent STDs.
By this method there is no direct contact of genital organs of male and female and thus it prevents transmission of any infection.
Question. “Variations” are seen in the organisms. State the two main causes of variation.
Answer : Variations are caused by:
a. Change in the genetic material, i.e., DNA at the time of DNA copying.
b. Environmental factors viz., light, temperature, nutrition, wind and water supply, etc.
c. Mutations.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Give reasons as to why the following processes are different from each other:
a. Fission in Amoeba and Plasmodium .
b. Binary fission and Fragmentation.
Answer : a. In Amoeba during binary fission the cell divides into two daughter cells while in Plasmodium multiple fission occurs, where the cell divides into many daughter cells.
b. In binary fission, a cell divides into two daughter cells while in fragmentation, the body of a multicellular organisms divides into two or more parts which grow further.
Question. Why is vegetative propagation practised for growing some types of plants?
or
Why is vegetative propagation practiced for growing some types of plant? List two plants which are grown by this method.
Answer :Advantages of vegetative propagation:
a. The plants bear flowers and fruits earlier than those propagated sexually.
b. Plants have lost capacity to form seeds hence they are propagated vegetatively. Such plants are genetically similar to parent plants and have all their characters.
Question. What does the diagram given below correctly illustrate? Give reason in support of your answer.
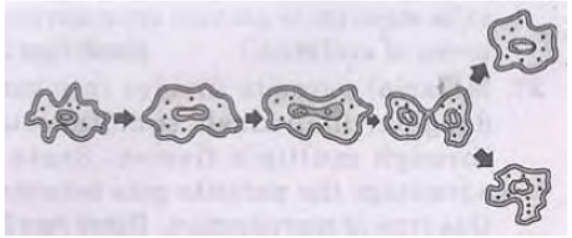
Answer : Binary fission in Amoeba. The splitting of the two cells during division in Amoeba can take place in any plane.
Question. What happens to the following parts after fertilization?
a. ovum
b. ovary
c. ovule
d. sepals and petals
Answer : a. forms zygote
b. forms fruit
c. forms seed
d. shrinks and fall off
Question. What is the function of copper-T used by some women? What is its effect?
Answer : Copper-T prevents pregnancy as it prevents implantation in the uterus. It can cause side effect due to irritation of the uterus.
Question. “The chromosomal number of the sexually producing parents and their offspring is the same.” Justify this statement.
Answer : a. DNA copying is essential for formation of addition cellular apparatus, so that when DNA copies separate, each cell gets its own cellular apparatus.
b. The process of DNA copying results in variation each time. As a result, the DNA copies generated will be similar, but may not be identical to the original.
Question. State the changes that take place in the uterus when
a. implantation of embryo has occurred
b. female gamete/egg is not fertilized
Answer : a. Uterus wall becomes thicker due to development of blood vessels and glands in it and placenta develops from the side of foetus so that it can derive nutrition from mother and pass the waste to mother’s blood.
b. Uterus lining gets peeled and shed off along with mucus, blood, dead ovum during menstruation.
Question. State the basic requirement for sexual reproduction. Write the importance of such reproduction in nature.
Answer : Sexual reproduction takes place in multicellular organisms with complex body design. There are specialized (sex) organs in which through a special type of cell division, number of chromosome is reduced to half and male and female germ cells/gametes form. These gamete fuse to form zygote on fertilization, thus the characteristic number of chromosome and the normal DNA content for a cell is regained. Sexual reproduction gives rise to more variations which are essential for evolution as well as survival of species under unfavorable conditions. Species reproducing sexually have better chances of survival.
Question. Mention one function each of the following parts with respect to the female reproductive system:
a. Vagina
b. Ovary
Answer : a. The uterus open into vagina through the cervix. The sperms enter through the vaginal passage during sexual intercourse.
b. One egg (female gamete) is produced every month by one of the ovaries.
Question. List and explain in brief three methods of contraception.
or
List any four methods of contraception. How are they helpful to young couples?
Answer : Four methods of contraception:
a. Condoms
b. Copper-T
c. Diaphragm
d. Oral pills
All these help in family planning as it helps in keeping gap between two children. They help in proper utilization of family resources.
Question. What happens when:
a. Accidentally Planaria is cut into three different pieces.
b. Bryophyllum leaf fall on the wet soil.
c. On maturation sporangia of Rhizopus burst.
Answer : a. Three new Planaria will form due to regeneration.
b. New plantlets will form from these buds helping the plant to propagate vegetatively.
c. Spores are released which upon finding suitable substratum germinates to form new individual.
Question. List four steps in sexual reproduction. Write two of its advantages.
Answer : a. Four steps in sexual reproduction :
b. Formation of gametes in the sex organs.
c. Transfer of male gamete to female gamete which involves release of both types of gametes in the medium outside.
d. Fusion of gametes, either inside or outside the female parents body.
e. Development of zygote to embryo and then complete individual.
Advantages:
a. Variations are produced among the progeny.
b. Such populations are able to adapt well to changing environment and thus evolves faster.
Question. List four categories of contraceptive methods. State in brief two advantages of adopting such preventive methods.
Answer : Four categories of contraceptive methods are:
a. Barrier method (Condoms)
b. Surgical method (Vasectomy in males and Tubectomy in females)
c. Withdrawal method
d. Calendar method
e. Hormonal method
f. IUCD/Copper-T/Loop (any four)
Two advantages:
a. Helps in maintaining health of women.
b. Helps in preventing STDs especially AIDS.
c. Helps in birth control.
Question. List any two modes of asexual reproduction. Under which mode of reproduction is vegetative propagation placed and why? List two advantages of vegetative propagation.
Answer : Two modes of asexual reproduction are fission Regeneration Vegetative propagation is placed under asexual reproduction as reproduction happens from any part of a plant. It may be either leaf, shoot or root.
Advantages are:
a. The plants bear flowers and fruits earlier than those propagated sexually.
b. Plants have lost capacity to form seeds hence they are propagated vegetatively.
Question. Write one main difference between asexual and sexual mode of reproduction. Which species is likely to have comparatively better chances of survival - the one reproducing asexually or the one reproducing sexually? Give reason to justify your answer.
Answer :
The species having sexual mode of reproduction have better chances of survival because sexual reproduction leads to variations which give better survival advantage to the species over time.
Question. Explain the term “Regeneration” as used in relation to reproduction of organisms. Describe briefly how regeneration is carried out in multicellular organisms like Hydra.
Answer : The ability to give rise to new individuals from the body parts of the parent individual is called regeneration, e.g., Hydra and Planaria, if their bodies get broken into many pieces, each piece is capable of re-growing into a complete individual.
Question. What is vegetative propagation? List two advantages and two disadvantages of vegetative propagation.
Answer : Method of producing new plants from vegetative parts like roots, stem and leaves is called vegetative propagation.
Advantages are:
a. The plants bear flowers and fruits earlier than those propagated sexually.
b. Plants have lost capacity to form seeds hence they are propagated vegetatively.
Disadvantages are:
a. Such plants are genetically similar to parent plants and are vulnerable to infections and diseases.
b. They do not have variations therefore do not adapt well to changing environment, the plant species does not evolve.
Question. Study the diagram given below:
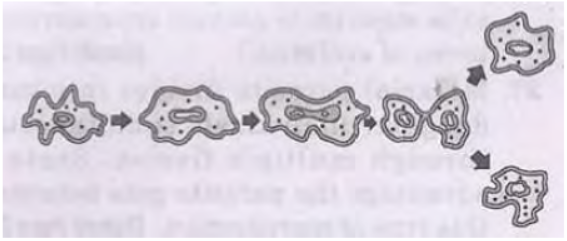
a. Identify the process.
b. Which organism uses the above method of reproduction?
c. How is the above method different from the process of fragmentation?
or
In context of reproduction of species, state the main difference between fission and fragmentation. Also give one example of each.
Answer : a. Binary fission.
b. Amoeba.
c. Binary fission occurs in unicellular organisms only. In fragmentation the body of a simple multicellular organism breaks down into many ‘fragments’. All cells undergo division and the organism develops from each fragment.
Question. Give the functions of the following in the process of reproduction:
a. Pollen tube.
b. ovary,
c. Stigma.
Answer : a. Pollen tube carries male gamete from stigma to ovule.
b. Ovary has ovule and forms fruit to protect and dispersal of seeds.
c. Stigma receives pollen during pollination.
Question. What does HIV stand for? Is AIDS an infectious disease? List any four modes of spreading AIDS.
Answer : HIV stands for Human Immunodeficiency Virus.
Yes, AIDS is an infectious disease.
Four modes of spreading AIDS are as follows:
(i) By having sexual contact with an infected person.
(ii) By the transfusion of blood from an infected person.
(iii) Through infected needles used for injection.
(iv) Through the placenta from the mother to child during pregnancy.
Question. (a) Explain the terms: (i) Implantation (ii) Placenta
(b) What is the average duration of human pregnancy?
Answer : (a) (i) Implantation: The embedding of a fertilised mammalian egg (embryo) into the inner thick wall of the uterus (womb) where it will continue its development is called implantation.
(ii) Placenta: It is a complex double-layered spongy vascular tissue in human female formed by the joint activity of maternal and foetal tissues in the wall of uterus that is meant for attachment, nourishment and waste disposal for the foetus.
(b) The average duration of human pregnancy is 40 weeks or 280 days.
Question. Write the full form of DNA. Name the part of the cell where it is located. Explain its role in the process of reproduction of the cell.
Answer : The full form of DNA is deoxyribonucleic acid. It is the genetic material found in the chromosomes, which are present in the nucleus of a cell.
DNA plays an important role in the reproduction of a cell. The reproducing cell produces an identical copy of DNA through some cellular mechanism. Since the newly formed copy of DNA lacks an organised cellular structure, the cell gets divided to provide cell cover to the newly formed DNA. Thus, two daughter cells are formed from the single cell as a result of the copying of DNA.
Question. Draw a diagram of a human female reproductive system and label the part
(i) that produces egg
(ii) where fusion of egg and sperm take place
(iii) where zygote is implanted
What happens to human egg when it is not fertilised?
Answer :
If the egg is not fertilised, the thick and nourishing lining of the uterus breaks and comes out through vagina as blood and mucous.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question. Explain vegetative propagation with the help of two examples. List two advantages of vegetative propagation.
Answer : In vegetative propagation, new plants are obtained from the parts of old plants like stems, roots and leaves, without the help of any reproductive organ.
There are two ways of vegetative propagation:
(a) Natural Vegetative Propagation, and
(b) Artificial Vegetative Propagation.
Natural vegetative propagation by leaves: The fleshy leaves of Bryophyllum bear adventitious buds in the notches along the leaf margin.
Grafting: In this method of reproduction, two plants of closely related varieties are joined together so that they live as one plant.
• The portion of a plant that is grafted on the other plant is called scion, and the plant in which grafting is performed is called the stock.
• This method is applied to improve variety of fruits like mango, apple, peas, citrus and guava. advantages of vegetative propagation are:
(i) Vegetative propagation is a cheaper, easier and more rapid method of propagation in plants than growing plants from their seeds.
(ii) Better quality of the plants can be maintained by this method.
Question. Describe in brief the role of (i) testis (ii) seminal vesicle, (iii) vas deferens, (iv) ureter and (v) prostate gland in human male reproductive system.
Answer : 1. Testis: Testes are oval shaped primary reproductive organs in The function of testes is to produce sperms and male sex hormone testosterone. The scrotum provides optimal temperature for the formation of sperms.
2. Seminal vesicle: Seminal vesicles are a pair of thin walled muscular elongated sac which secrete fluid for nourishment of sperms.
3. vas deferens: The sperms are carried by a long tube called vas deferens to organs called seminal vesicles where the sperms get nourishment and stored.
4. Ureter It is the tube that carries urine from kidney to the urinary bladder. In humans, there are two ureters, one attached to each kidney.
5. Prostate glands: Prostate glands produce a fluid which is released in the urethra along with secretion of seminal vesicles for nourishment and transportation of sperms.
Question. List any three differences between pollination and fertilisation.
Answer :
Question. Illustrate the following with the help of suitable diagrams:
(i) Binary Fission in Amoeba.
(ii)Leaf of Bryophyllum with buds.
Answer :
Question. a. Name the human male reproductive organ that produces sperms and also secretes a hormone. Write the functions of the secreted hormone.
b. Name the parts of the human female reproductive system where
(i) Fertilization takes place,
(ii) Implantation of the fertilized egg occurs.
Explain how the embryo gets nourishment inside the mother’s body.
Answer : a Testis - secrete male hormone - testosterone.
Functions : (i) Formation of sperms, (ii) Development of secondary sexual characters.
b. (i) fallopian tube/oviduct. (ii) uterus.
Placenta is a special disc like tissue embedded in the mother’s uterine wall and connected to the foetus/embryo. Placenta provides a large surface area for glucose and oxygen/ nutrients to pass from the mother’s blood to the embryo/ foetus.
Question. a. List two reasons for the appearance of variations among the progeny formed by sexual reproduction.
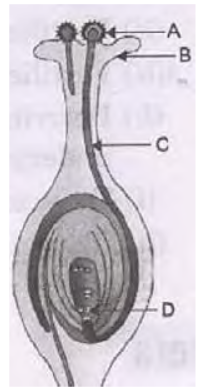
b. (i) Name the part marked A in the diagram.
(ii) How does “A” reaches part B?
(iii) State the importance of , the part C.
(iv) What happens to the part marked D after fertilization is over?
Answer : a. Sexual reproduction confers new characteristics on the offspring due to genetic recombination occurring during gamete formation in the sex organs. Moreover it involves union of two gametes coming from two parents which different genetic combination. Thus it ensures more diversity in characteristics.
b. (i) Pollen
(ii) Pollination
(iii) Pollen tube carries male gametes to the ovule in ovary.
(iv) Ovule turns into seeds.
Question. a. (i) Write full form of DNA.
(ii) State the role of DNA in the cell nucleus,
(iii) What will be the after effect if the information of the DNA is changed.
b. Explain the importance of DNA copying in reproduction.
Answer : a. (i) Deoxyribo Nucleic Acid.
(ii) Informational source for making proteins.
(iii) Proteins will be changed.
b. Its only due to DNA copying that body designs are similar because DNA cell nucleus carries information for making proteins if DNA copying will not take place then body design will change.
Question. a. Draw a diagram of the longitudinal section of a flower and label on it sepals, petal, ovary and stigma.
b. Write the names of male and female parts of a flower.
Answer : a.
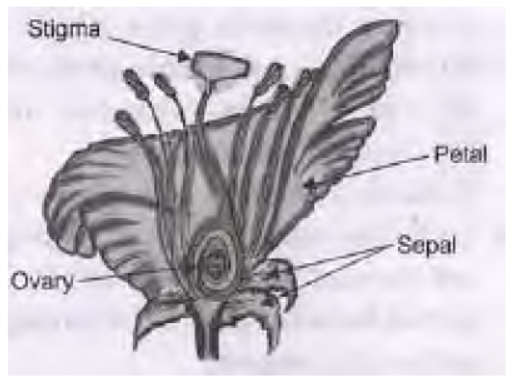
b. Male Part : Stamen; Female Part : Carpel/pistil
Question. Define the following processes:
a. Fertilization
b. Menstruation
c. Binary fission
d. Vegetative propagation
e. Regeneration
Answer : a. The fusion of male gamete with female gamete is known as fertilization.
b. Menstruation cycle takes place every month when egg is not fertilized. It lasts for about two to eight days and during this cycle the lining of uterus slowly breaks and comes out through the vagina as blood and mucus.
c. Binary fission is the splitting of nucleus into two daughter cells which can take place in any plane. It can be observed in Amoeba.
d. When vegetative part of a plant like the root, stem or leaves develops into new plant under appropriate conditions, it is known as vegetative propagation.
e. When body of an organism cuts into any number of pieces and each piece grows into a complete organism. This is known as regeneration. Hydra and Planaria reproduce through this process.
Case Based Questions :
Read the following passage and answer questions from X, Y and Z are three sexually transmitted diseases (STDs). X and Z are caused by bacteria whereas Y is caused by virus P. Virus P lowers the immunity of a person and leads to an incurable disease. X starts as painless sores on genitals rectum or mouth. Z causes painful urination and abnormal discharge from genitals.
Question. Select the incorrect statement regarding diseases X and Y.
(a) Both X and Y can spread from infected mother to unborn baby during pregnancy.
(b) Both X and Y can spread from infected partner to healthy partner by unprotected sex.
(c) Y can also spread through use of contaminated needles and blood transfusion.
(d) None of these
Answer : D
Question. How can disease Y be prevented?
(a) By following polygamy and having protected sex.
(b) Use of sterilised needles for injecting medicines, blood tests, etc.
(c) Collecting blood from unknown donors without background check by blood bank professionals.
(d) All of these
Answer : B
Question. Select the option that correctly identifies disease X, Y and Z?
X Y Z
(a) AIDS Syphilis Gonorrhoea
(b) Syphilis AIDS Gonorrhoea
(c) Gonorrhoea Syphilis AIDS
(d) Syphilis Gonorrhoea AIDS
Answer : B
Question. Identify virus P from the given paragraph.
(a) Human papilloma virus
(b) Human adenovirus
(c) Human immunodeficiency virus
(d) Human cytomegalovirus
Answer : C
Question. What are the symptoms of disease Y?
(a) Weight loss
(b) Fever or night sweats
(c) Fatigue and weakness infections
(d) All of these
Answer : D
Read the following passage and answer questions from P and Q are two monoecious plants. P bears bisexual flowers whereas Q bears unisexual flowers. P does not need a pollinating agent whereas pollinating agent is required in case of Q.
Question. Which of the following holds true for plant Q?
(a) Plant Q bears complete flowers.
(b) Plant Q bears either male flowers or female flowers but never both.
(c) Sexual reproduction in plant Q may or may not give rise to genetic variations.
(d) All of these
Answer : C
Question. Select the correct statement.
(a) Flowers of plant P produce large number of pollen grains as compared to flowers of plant Q.
(b) Sexual reproduction in plant P does not bring variations.
(c) Sexual reproduction in plant P often gives rise to new varieties due to accumulation of genetic variations.
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer : B
Question. Select the option that correctly identifies plant P and Q.
(a) P - Papaya, Q - Marigold
(b) P - Pea, Q - Cucurbit
(c) P - Sunflower, Q - Orchid
(d) P - Tulip, Q - Daffodil
Answer : B
Question. Select the correct option regarding plants P and Q.
(a) Seed setting is assured in plant P even if all its flowers are emasculated.
(b) Male flowers of plant Q always open only after the female flowers of the plant are pollinated.
(c) Female flowers of plant Q can reproduce by cross pollens or self pollens depending upon the genus to which plant Q belongs to.
(d) P is a cross pollinated plant whereas Q is a self pollinated plant.
Answer : C
Question. How can self pollination be avoided in plant P? B
(a) By removing all the flowers of plant P
(b) By removing all the anthers of all the flowers
(c) By removing all the carpels of all the flowers
(d) None of these
Answer : B
| CBSE Class 10 Science Chemical Reactions and Equations VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Science Acids Bases and Salts VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Science Metals and Non metals VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Science Carbon and its Compounds VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Science Periodic Table VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Science Life Processes VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Science Control and Coordination VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Science How Do Organisms Reproduce VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Science Heredity and Evolution VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Science Light Reflection and Refraction VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Science Human Eye and Colourful World VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Science Electricity VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Science Magnetic Effects of Electric Current VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Science Sources of Energy VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Science Our Environment VBQs |
| CBSE Class 10 Science Sustainable Management of Natural Resources VBQs |
VBQs for Chapter 8 How do the Organisms Reproduce Class 10 Science
We hope students liked the above VBQs for Chapter 8 How do the Organisms Reproduce designed as per the latest syllabus for Class 10 Science released by CBSE. Students of Class 10 should download the Value Based Questions and Answers in Pdf format and practice the questions and solutions given in above Class 10 Science VBQs Questions on daily basis. All latest VBQs with answers have been developed for Science by referring to the most important and regularly asked topics which the students should learn and practice to get better score in school tests and examinations. Expert teachers of studiestoday have referred to NCERT book for Class 10 Science to develop the Science Class 10 VBQs. After solving the questions given in the VBQs which have been developed as per latest course books also refer to the NCERT solutions for Class 10 Science designed by our teachers. We have also provided a lot of other VBQs for Class 10 Science which you can use to further make yourself better in Science.
You can download the CBSE VBQs for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 How do the Organisms Reproduce for latest session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the VBQs issued by CBSE for Chapter 8 How do the Organisms Reproduce Class 10 Science have been made available here for latest academic session
There is no charge for the VBQs and their answers for Class 10 CBSE Science Chapter 8 How do the Organisms Reproduce you can download everything free
Regular revision of VBQs given on studiestoday for Class 10 subject Science Chapter 8 How do the Organisms Reproduce can help you to score better marks in exams
Value Based Questions (VBQs) for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 How do the Organisms Reproduce help to test the ability of students to apply learnings to various situations in life.

