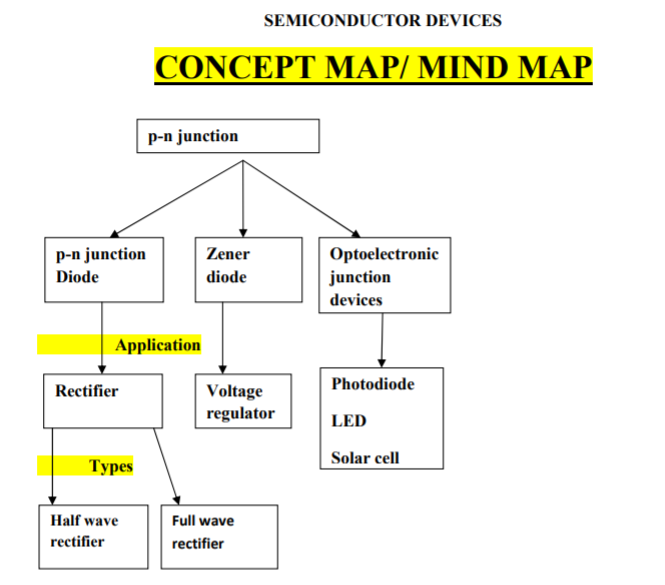
CBSE Class 12 Physics Semi Conductor Devices Concept Map. Please refer to the examination notes which you can use for preparing and revising for exams. These notes will help you to revise the concepts quickly and get good marks.
Semi Conductor MCQ Questions with Answers Class 12 Physics
Q.- Major parts of a communication system are :
(a) transmitter and receiver
(b) receiver and communication channel
(c) transmitter and communication channel
(d) transmitter, receiver and communication channel
Ans-(d)
Q.- Communication channel consists of :
(a) transmission line
(b) optical fibre
(c) free space
(d) all of these
Ans- (d)
Q.- Audio frequency range is from :
(a) 20 Hz to 20 kHz
(b) 200 Hz to 2000 Hz
(c) 2k Hz to 20 kHz
(d) 20 kHz to 200 kHz
Ans-(a)
Q.- Basic components of a transmitter are :
(a) message signal generator and antenna
(b) modulator and antenna
(c) signal generator and modulator
(d) message signal generator, modulator and antenna
Ans-(d)
Q.- Range of frequencies allotted for commerical FM radio broadcast is :
(a) 88 to 108 MHz
(b) 88 to 108 kHz
(c) 8 to 88 MHz
(d) 8 to 88 kHz
Ans-(a)
6. The most commonly used two wire lines are :
(a) parallel wire lines
(b) twisted pair wire lines
(c) co-axial wire lines
(d) all of these
Ans- (d)
Q.- A digital signal possesses :
(a) continously varying values
(b) only two discrete values
(c) only four discrete values
(d) none of the above
Ans-(b)
Q.- Modern communication systems are :
(a) analog circuits
(b) digital circuits
(c) combination of analog and digital
(d) none of the above
Ans-(b)
Q.-In frequency modulation :
(a) the amplitude of modulated wave varies as frequency of carrier wave
(b) the frequency of modulated wave varies as amplitude of modulating wave
(c) the amplitude of modulated wave varies as amplitude of carrier wave
(d) the frequency of modulated wave varies as frequency of modulating wave
Ans-(b)
Q.- The principal used for the transmission of light signals through the optical fibre is :
(a) reflection
(b) refraction
(c) interference
(d) total internal relfection
Ans-(d)
Q.- Modulation is the process of superposing :
(a) low frequency audio signal on high frequency waves
(b) low frequency radio signal on low frequency audio waves
(c) high frequency radio signal on low frequency audio signal.
(d) high frequency audio signal on low frequency radio waves
Ans-(a)
Q.- What happens inside optical fibres ?
(a) Diffraction
(b) Polarization
(c) Interference
(d) Total internal reflection
Ans-(d)
Q.- In frequency modulated wave
(a) frequency varies with time
(b) amplitude varies with time
(c) both frequency and amplitude varies with time.
(d) both frequency and amlitude are time.
Ans-(a)
Q.- An oscillator is producing FM waves of frequency 2 kHz with a variation of 10 kHz. What is the modulating index ?
(a) 0.02
(b) 5.0
(c) 0.67
(d) 1.5
Ans-(b)
Q.- For effective modulation and transmission of message signal, which one of the following condition is true ?
(a) Frequency of message signal < frequency of carrier wave
(b) Frequency of message signal > frequency of carrier wave
(c) Amplitude of message signal > amplitude of carrier wave
(d) Amplitude of message signal < amplitude of carrier wave
Ans-(a)
Q.- Which of the following device is full duplex ?
(a) Mobile phone
(b) Walky-talky
(c) Loud speaker
(d) Radio
Ans-(a)
Q.-Modulation is the phenomenon of :
(a) superimposing the audio frequency signal over a carrier wave
(b) separating the audio frequency signal from the carrier wave
(c) separating carrier wave from the modulated wave
(d) any of (a), (b), or (c)
Ans-(a)
Q.-The modulating frequency is 5 kHz and the carrier frequency is 100 kHz. What is the band width of AM transmission ?
(a) 105 KHz
(b) 95 kHz
(c) 2.5 kHz
(d) 10 kHz
Ans-(d)
Q.- Why is it difficult to transmit audio signals directly ?
(a) A very high antenna is needed for their propagation
(b) Audio signals have a very high frequency
(c) Audio signals can’t propagate independently
(d) Audio signals can’t propagate through air
Ans- (a)
Q.- Degree of modulation :
(a) can take any value
(b) should be less than 100%
(c) should exceed 100%
(d) none of the above
Ans-(b)
Q.- Demodulation is the :
(a) process of decoupling of modulating wave from the carrier wave
(b) process of coupling modulated wave with modulating
(c) process of separating carrier wave from the modulated wave
(d) process of combining the message signal with the carrier wave
Ans-(a,c)
Q.-For transmitting audio signal properly :
(a) it is first superimposed on high frequency carrier wave
(b) it is first superimposed on low frequency carrier wave
(c) it is sent directly without superimposing on any wave
(d) none of the above
Ans-(a)
Q.- If a carrier wave of 1000 kHz is used to carry the signal, the length of transmitting antenna will be equal to :
(a) 3 m
(b) 30 m
(c) 300 m
(d) 3000 m
Ans-(c)
Q.-The types of modulation which are possible, are :
(a) one only
(b) two only
(c) three only
(d) none of these
Ans-(c)
Q.-The sky wave propagation is suitable for radio-wave of frequency :
(a) upto 2 MHz
(b) from 2 MHz to 20 MHz
(c) from 2 MHz to 30 MHz
(d) from 2 MHz to 80 MHz
Ans-(c)
Q.-An antenna is of height 500 m. What will be its range (Radius of earth is 6400 km) ?
(a) 800 km
(b) 100 km
(c) 50 km
(d) 80 km
Ans-(d)
Q.-Refractive index of ionosphere is :
(a) zero
(b) more than one
(c) less than one
(d) one
Ans-(c)
Q.- The ground wave propagation is suitable for radio waves of frequency :
(a) upto 2 MHz
(b) from 2 MHz to 20 MHz
(c) from 2 MHz to 30 Hz
(d) none of these
Ans-(a)
Q.- The electromagnetic waves of frequency 80 MHz to 200 MHz :
(a) can be reflected by troposphere
(b) can be reflected by ionosphere
(c) can be reflected by mesophere
(d) can not be reflected by any layer of earths atmosphere
Ans-(d)
Q.- Acceptor atoms introduced into a pure semiconductor at room temperature :
(a) increase the number of electrons in the conduction band
(b) increase the number of holes in the valence band
(c) lower the Fermi level.
(d) increase the electrical resistivity.
Ans-(b)
Q.- Which of the following is NOT true when a reverse bias is applied to a p-n junction ?
(a) Electrons flow from the p to the n side.
(b) Holes flow from the p to the n side.
(c) the electric field in the depletion zone increases
(d) The potential difference across the depletion zone increases
Ans-(b)
Q.- A p-n photodiode is fabricated from a semiconductor with a band gap of 2.5 eV. It can detect a signal of wavelength:
(a) 4000 nm
(b) 6000 nm
(c) 4000 Å
(d) 6000 Å
Ans-(b)
Q.- When germanium is doped with phosphorus, the doped material has :
(a) excess positive charge
(b) excess negative charge
(c) more negative current carriers
(d) more positive current carriers
Ans-(c)
Q.- Which of the following statement is correct for an n-type semiconductor?
(a) The donor level lies below the bottom of the conduction band
(b) The donor level lies closely above the top of the valence band
(c) The donor level lies at the halfway mark of the forbidden energy gap
(d) None of the above
Ans-(a)
Q.- In a p-type semiconductor, the majority and minority charge carriers are respectively,
(a) protons and electrons
(b) electrons and protons
(c) electrons and holes
(d) holes and electrons
Ans-(d)
Q.- In an n-p-n circuit transitor, the collector current is 10 mA.If 80% electrons emitted reach the collector, then :
(a) the emitter current will be 7.5 mA
(b) the base current will be 2.5 mA
(c) the base current will be 3.5 mA
(d) the emitter current will be 15 mA
Ans-(b)
Q.- Due to diffusion of electrons from n to p-side,
I. electron-hole combination across p-n junction occurs.
II. an ionised acceptor is left in the p-region.
III. an ionised donor is left in the n-region.
IV. electrons of n-side comes to p-side and electron-hole combination takes palce in p-side Correct options are :
(a) I and II
(b) II and III
(c) II and IV
(d) II, III and IV
Ans-(d)
Q.- Assertion : NAND or NOR gates are called digital building blocks.
Reason : The repeated use of NAND (or NOR) gates can produce all the basic or complicated gates.
(a) A
(b) B
(c) C
(d) D
Ans-(a)
Q.- Assertion : The color of light emitted by a LED depends on its forward biasing.
Reason : The reverse biasing of p-n junction will increase the width of depletion layer.
(a) A
(b) B
(c) C
(d) D
Ans-(d)
Q.- Assertion : The resistance of an intrinsic semiconductor decreases with the increase in temperature.
Reason : The concentration of electrons becomes more than the concentration of holes in an intrinsic semiconductor when heated.
(a) A
(b) B
(c) C
(d) D
Ans-(a)
Please click the link below to download pdf file of CBSE Class 12 Physics Semi Conductor Devices Concept Map.

