TOPIC: ACIDS, BASES & SALTS
Important Revision Notes on Acids Bases and Salts
Acid :- Acid is a compound which when dissolves in water furnishes hydronium ion(H3O+) as the only positively charged ion.
Classification of the Acid :-
(A) Depending on their Source :-
(i) Organic Acid :- Acids which are obtained from plants and animals are called organic acid.
Eg:- Oxalic acid (COOH)2
Formic acid (HCOOH)
Acetic acid (CH3COOH)
The contain carbon atom along with hydrogen atom.
They are weak acid and they do not completely ionizes hence they contain ions as well as molecules
(ii) Inorganic/ Mineral Acid :- They are obtained from minerals. Eg:- Nitric Acid, Sulphuric Acid etc.
They are strong acid and they completely ionizes. Hence the solution obtained contains high concentration of hydronium ion.
These acid do not contain carbon except carbonic acid.
Carbonic Acid is a weak mineral acid which contain molecules.
Acid containing hydrogen and a non metallic element and do not contain oxygen are referred as hydra acid. Eg:- Hydrochloric acid ( HCL), Hydrobromic acid ( HBr)
Acid containing hydrogen and a non metallic element and contain oxygen are referred as oxy acid eg HNO3, H2SO4
(B) Depending on their basicity :- Basicity of an acid if defined as number of hydronium ions that can be produced by the ionisation of one molucules of that acid in aqueous solution
(i) Mono Basic Acid :- Acid which on ionisation in water produces one hydronium ion per molecule of the acid. Eg : HCL, HBr, HNO3, CH3COOH
(ii) Dibasic acid Eg:- Sulphuric acid (H2SO4) , Carbonic Acid ( H2CO3), Oxalic acid (H2C2O4),
NOTE :- H3PO3 is a Dibasic acid because of its structure .
(iii) Tribasic Acid :- Phosphoric Acid (H3PO4)
NOTE :- SILICIC ACID ( H4SiO4 ) has basicity 4
(C) Concentration of the Acid: The amount of water present in a given sample of the acid is called concentration. It is divided into two parts
(i) Concentrated Acid : A sample which contain little or no amount of water.
(ii) Dilute Acid : An acid which contain large amount of water
(D) Strength of the Acid: It is defined as the amount of hydronium ion (H3O+) generated in a given time interval. The acid which undergoes complete ionization in aqueous solution . Therefore producing high concentration of hydronium ion are called strong acid eg HCl, HNO3, H2SO4
The acid which undergoes partial ionization in aqueous solution are called weak acid . eg CH3COOH,
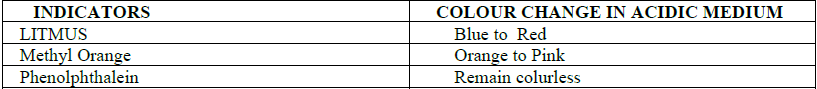
(E) Action on indicators
BASE : Those compounds which reacts with hydronium ion to form salt and water as the only product According to this definition metallic oxide/hydroxide (CuO,MgO,Cu(OH)2 ) comes into this category.
CuO + 2 HCl ——> CuCL2 + H2
But according to this definition PbO2 and MnO2 are not considered as base because both the compounds when reacted with HCl liberate chlorine gas along with salt and water.
PbO2 + 4HCl ——>PbCl2 + 2H2O + Cl2
MnO2 + 4HCl ——>MnCl2 + 2H2O + Cl2
Alkali : They are those bases which are soluble in water and produces hydroxyl ion ( OH-) as the only negatively charged ion.
NaOH ——>Na +1 + OH-1
NH4OH ——>NH4+1 + OH-1
According to this definition bases have to be soluble in water then only they would be reffered as alkali for eg Cu( OH)2 and Fe(OH)3 are bases but they are not alkali because they are insoluble in water . Hence all alkali are bases but all bases are not alkali.
Classification of Alkali
(A) On the basis of acidity: The number of hydroxyl ion (OH-) that can be produced per molecule of the base in aqueous solution
(i) Monoacidic base : NaOH, KOH, NH4OH
(ii) Diacidic base : Ca(OH)2
(iii) Triacidic base : Al(OH)3
(B) Action on indicators
pH of solution : It is the negative logarithm to the base 10 of the hydronium ion concentration expressed in moles per litre
If pH = 7 then the solution is neutral
If pH < 7 then the solution is acidic
If pH > 7 then the solution is alkaline
Universal Indicatores : It give different colours to different concentrations of hydronium ion in solution
Salts : A compound formed by neutralization of an acid with a base is called a salt
(i) Normal salt : The complete replacement of hydrogen ions of an acid by a base .
(ii) Acidic salt : The partial/incomplete replacement of hydrogen ion of an acid by a base.
(iii) Basic salt: The partial/incomplete replacement of hydroxyl ion of a base by an acid.
Question : 1. Differentiate between organic acids and mineral acids. Give two examples each.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Question : 2. When turmeric stain gets on a white cloth & the cloth is cleaned with soap, the stain becomes red. Why? How can one remove the red stain?
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Question : 3. a) How are salts formed?
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
b) How do salts differ from acids and bases?
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
c) Name two salts which are commonly used at home.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Question : 4. Write an example for the word equation for the neutralization reaction.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Question : 5. What are alkalis?
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Question : 6. Why are antacids used in daily life?
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Question : 7. You are provided with three test tubes. Tube A contains lemon juice, tube B contains soap solution and tube C contains pure water. What will you observe when you put a piece of
i. blue litmus paper in each of the test tube.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
ii. red litmus paper is put into each of the test tube.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
iii. a few drops of china rose indicator into each of the test tubes.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Question : 8. Is distilled water acidic /basic or neutral? How would you verify it?
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Question : 9. Disposal of factory waste in water bodies has been found to be harmful to aquatic plants and animals. What should the factory owners do to prevent the above ill effect?
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Question : 10. How does rain water become acidic?
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Please click on below link to download CBSE Class 7 Science Acid Bases And Salts Worksheet Set D

