CHEMICAL KINETICS
OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS
Multiple choice type questions
1. The term – dc/dt in a rate equation refers to :
(a) the conc. of a reactant
(b) the decrease in conc. of the reactant with time
(c) the velocity constant of reaction
(d) None of these
2. Order of reaction can be
(a) 0 (b) fraction
(c) whole number (d) integer, fraction, zero
3. Instantaneous rate of a chemical reaction is
(a) rate of reaction in the beginning
(b) rate of reaction at the end
(c) rate of reaction at a given instant
(d) rate of reaction between two specific time intervals
4. Which one of the following statements for the order of a reaction is incorrect ?
(a) Order can be determined only experimentally.
(b) Order is not influenced by stoichiometric coefficient of the reactants.
(c) Order of reaction is sum of power to the concentration terms of reactants to express the rate of reaction.
(d) Order of reaction is always whole number.
5. The rate constant for the reaction
2N2O5 →4NO2 + O2 is 3.10 × 10–5 sec–1. If the rate is 2.4 × 10–5 mol litre–1 sec–1 then the concentration of N2O5 (in mol litre–1) is :
(a) 0.04 (b) 0.8
(c) 0.07 (d) 1.4
6. The rate law for a reaction between the substances A and B is given by Rate = k [A]n [B]m ..On doubling the concentration of A and halving the concentration of B, the ratio of the new rate to the earlier rate of the reaction will be as

7. In the reaction 2A + B →A2B, if the concentration of A is doubled and that of B is halved, then the rate of the reaction will:
(a) increase 2 times (b) increase 4 times
(c) decrease 2 times (d) remain the same
8. The rate constant of a reaction is 3.00 × 103 L mol–1 sec–1. The order of this reaction will be:
(a) 0 (b) 1
(c) 2 (d) 3
9. Half life of a first order reaction is 4s and the initial concentration of the reactant is 0.12 M. The concentration of the reactant left after 16 s is
(a) 0.0075 M (b) 0.06 M
(c) 0.03 M (d) 0.015 M
10. The rate constant of a first order reaction is 6.9x10-3s-1 .How much time will it take to reduce the initial concentration to its 1/8th value?
(a) 100 s (b) 200 s
(c) 300 s (d) 400 s
11. A reaction proceeds by first order, 75% of this reaction was completed in 32 min. The time required for 50% completion is
(a) 8 min (b) 16 min
(c) 20 min (d) 24 min
12. In a first-order reaction A → B, if k is rate constant and inital concentration of the reactant A is 0.5 M, then the half life is
13. The value of rate constant of a pseudo first order reaction _________.
(a) depends on the concentration of reactants present in small amount.
(b) depends on the concentration of reactants present in excess.
(c) is independent on the concentration of reactants.
(d) depends only on temperature.
14. A substance 'A' decomposes by a first order reaction starting initially with [A] = 2.00 M and after 200 min, [A] becomes 0.15 M. For this reaction t1/2 is
(a) 53.72 min (b) 50.49 min
(c) 48.45 min (d) 46.45 min
15. In a reaction the initial concentrations of the reactants increase fourfold and the rate becomes eight times its initial value. The order of the reaction is
(a) 2.0 (b) 3.5 (c) 2.5 (d) 1.5
16. The unit of the rate of reaction is the same as that of the rate constant for a
(a) zero-order reaction (b) first-order reaction
(c) second-order reaction (d) half-order reaction
17. For a first-order reaction, the time required for 99.9% of the reaction to take place is nearly
(a) 10 times that required for half the reaction
(b) 100 times that required for two-thirds of the reaction
(c) 10 times that required for one-fourth of the reaction
(d) 20 times that required for half of the reaction
18. For the reaction 2N2O5 → 4NO2 + O2, rate and rate constant are 1.02 × 10–4 and 3.4 × 10–5 sec-1 respectively,then concentration of N2O5 at that time will be
(a) 1.732 (b) 3
(c) 3.4 × l05 (d) 1.02 × 10–4
19. Which one of the following equations is correct for the reaction N2 (g) + 3H2 (g) →2NH3 (g)?
20. The unit of rate constant depends upon the
(a) molecularity of the reaction.
(b) activation energy of the reaction.
(c) order of the reaction.
(d) temperature of the reaction
21. For a zero order reaction, the plot of concentration Versus time is linear with
(a) positive slope with zero intercept
(b) positive slope with non-zero intercept
(c) negative slope with non-zero intercept
(d) parallel to time axis
22. For the following reaction A (g) → B (g) + C (g) .The initial pressure was P0 while pressure after time ‘t’ was Pt. The rate constant k will be
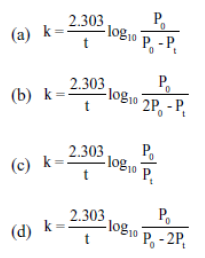
23. For a zero order reaction, the concentration of reactant after 10s is 0.2 mol/l. If k is 2 × 10– 2 mol l–1s–1, the initial concentration of reactant is
(a) 0.6 mol/l (b) 0.4 mol/l
(c) 0.8 mol/l (d) 1 mol/l
24. A reaction involving two different reactants can never be
(a) Unimoleculur reaction
(b) 1st order reaction
(c) 2nd order reaction
(d) Bimoleculur reaction
25. The rate constant of first-order reaction is 10–2 min–1.The half-life period of reaction is
(a) 693 min (b) 69.3 min
(c) 6.93 min (d) 0.693 min
26. For a chemical reaction which can never be a fractional number.
(a) order (b) half-life
(c) molecularity (d) rate constant
27. If we double the initial concentration ,for a certain first order reaction ,then t1/2 for the reaction
(a)will increase by two times
(b)will decrease by four times
(c) remains the same
(d)will decrease by half times
28. In a reaction 2A+B→A2B ,the reactant B will disappear at
(a) Half the rate as A will decreae
(b) The same rate as A will decrease
(c) Twice the rate as A will decrease
(d) Half the rate as A2B will form
29. A first order reaction is 50% completed in 1.26 × 1014 s. How much time would it take for 100% completion?
a) 1.26 × 1015 s (b) 2.52 × 1014 s
(c) 2.52 × 1028 s (d) Infinite
30. For a reaction A+B→ P , the rate is given by Rate =k[A][B]2 What is the overall order of reaction if A is present in large excess?
(a)3 (b)0
(c)2 (d)1
Fill in the blanks
31. The reaction which occurs in one step is known as _______________
32. In _______________,rate of reaction is independent of the concentration of the reactants.
33. For the reaction A → B, the rate of reaction becomes three times when the concentration of A is increased by nine times. The order of reaction is _______________
34. Rate constant is the rate of a reaction when concentration of reactants is _____________
35. The condition at which average rate can be equal to instantaneous rate of the reaction is_____________________
A statement of assertion is followed by a statement of reason. Mark the correct choice from the options given below:
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false but reason is true
36. Assertion : Molecularity has no meaning for a complex reaction.
Reason: The overall molecularity of a complex reaction is equal to the molecularity of the slowest step
37. Assertion : In rate law, unlike in the expression for equilibrium constants, the exponents for concentrations do not necessarily match the stoichiometric coefficients.
Reason : It is the mechanism and not the balanced chemical equation for the overall change that governs the reaction rate.
38. Assertion :The order of a reaction can have fractional value.
Reason : The order of a reaction cannot be written from balanced equation of a reaction.
39. Assertion: Hydrolysis of methyl ethanoate is a pseudo first order reaction.
Reason: Water is present in large excess and therefore its concentration remained constant throughout the reaction
40. Assertion: Half life of a reaction can be used to predict order of a reaction.
Reason: The relationship between half life and initial concentration of the reactant is dependant on order
Please click on below link to download CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chemical Kinetics Worksheet Set C

