“The best way to predict the future is to create it.” – Peter Drucker
Peter F. Drucker defined entrepreneur as one who always searches for an opportunity. The basic test of a successful entrepreneur is the identification of business opportunity in the environment and initiating steps to produce and sell goods and services to make the best use of that opportunity.
Q 1 What is a business opportunity?
There are a lot of opportunities in the world of business, which everyone might not be able to spot. An entrepreneur should be able to spot it. Business opportunity can be described as an economic idea which
can be implemented to create a business enterprise and earn profits.
Before selecting an opportunity, the entrepreneur has to ensure two things-
1. There is a good market for the product he is going to produce
2. The rate of return on the investment is attractive to be accepted by him Only when the entrepreneur is able to fulfil these two criteria, he/she can be successful. Quite often, a question arises - Can all ideas be converted into opportunities? Mostly entrepreneurs conceive an idea and start their business without even analysing the market which often leads to satisfying their own ego, and the result is that they launch a product that has very few customers.
Q2 List elements of a business opportunity
A business opportunity may be described as an attractive economic idea which could be implemented to create a business, earn profits and ensure further growth. A business opportunity has five elements which are as follows:
1. Assured market scope
2. An attractive and acceptable rate of return on investment
3. Practicability of the idea
4. Competence of the entrepreneur to encash it
5. Potential of future growth
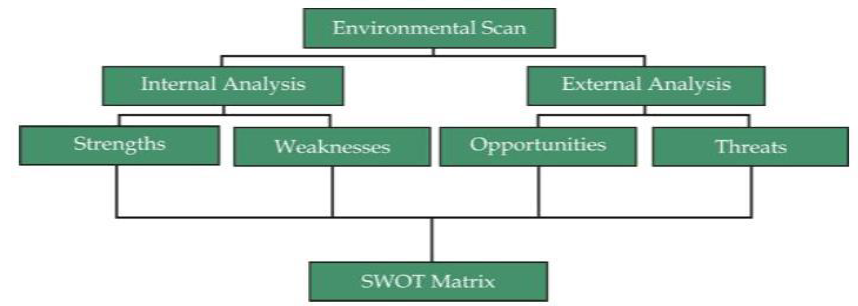
Q3 show in a diagram impact of the opportunities in the environment.
A prospective entrepreneur has to find an opportunity which would be suitable for him/her in terms of customers to be served and profits expected. An opportunity may be derived from the needs and problems of the society.
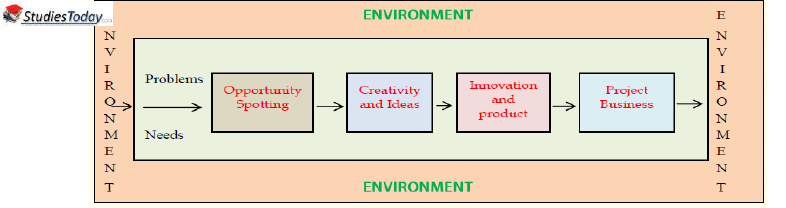
This diagram shows the following stages:
i) Opportunity spotting by analysing the needs and problems that exist in the environment
ii) Evaluating the ideas received from different sources to find a creative solution
iii) Identifying a product or service through innovation
iv) Setting up a project and nurturing it to success
Sensing entrepreneurial opportunities is thus a process of converting an idea into an opportunity and then into an enterprise. We can see clearly that the first stage is to spot the needs by looking into the needs and problems that exist. For example, in the second case study the text book (Refer Text book) on TravelKhana, we can clearly see that the entrepreneur struck on the idea of starting the venture when he faced problems himself, while travelling. It is then he saw the opportunity that people are ready to pay money for good quality food while travelling.
Q4 How entrepreneurs are perceiving and sensing opportunities?
The entrepreneurs perceive opportunities, synthesize the available information and analyse emerging patterns that escape the attention of other people. They are people with vision, capable of persuading others such as customers, partners, employees and suppliers to see the opportunity, share and support it.
Q5 explain the factors involved in sensing opportunities.
To sense an entrepreneurial opportunity, an entrepreneur employs his/her sharpened skills of observation, analysis and synthesis to identify an opening. The most important factors involved in the process are:
1. Ability to perceive and preserve basic ideas which could be used commercially
2. Ability to harness different sources of information
3. Vision and creativity
Ability to perceive and preserve basic ideas
Spotting an idea often triggers the process of sensing an opportunity. The following are the various sources which lead to the emergence of basic ideas.
(a) Problems: When a problem exists, an idea leads to a solution to resolve that problem, it emerges as a business opportunity.
(b) Change: A change in social, legal, technological aspects etc. leads to new opportunities to start a business.
(c) Inventions: New products or services leads to new business opportunities.
(d) Competition: Competition often results in emergence of new and better ideas that result in new business opportunities.
(e) Innovation: Creating new things of value as well as new and creative processes that add value to the existing products or services. For example, computers to tablets.
Ability to harness different sources of informationVarious sources like magazines, journals, books, seminars, trade shows, family members, customers, friends etc. help in getting information that results in evolution of basic ideas. Bring together various sources of information and knowledge, and analyze it to the best possible extent. The analysis helps in the identification of the right opportunity to start a new business. Vision and creativity
Creativity in innovating a solution and vision: The entrepreneur should be able to creatively identify an idea to generate a valuable solution to a problem. Once the solution is identified their vision to convert the solution into business opportunity helps them to move forward, overcoming all the obstacles. They constantly
a) Overcome adversity
b) Exercise control over the business
c) Make a significant difference.
Q 6 What is environment scanning?
Careful monitoring of an organization's internal and external environment for detecting early signs of opportunities and threats that may influence its current and future plans.
Q 7 Why do we need to scan our environment?
In a rapidly changing environment, one rule of thumb applies: If you don't adapt, you don't endure. This is the core idea behind environmental scanning. Definitions of the term refers to the means by which organizations gather information on changing conditions and incorporate those observations into a process where necessary changes are made. The right information, combined with the right adaptations, can determine an organization's future viability. If an entrepreneur is not aware of the environment surrounding his/her business, he/she is sure to fail.
Q8 Explain the importance of environment.
Sensitivity to environmental factors is crucial for an entrepreneur. If a company is able to adapt to its environment, it would succeed in the long run. For example, Sony is failing to understand the changing trends in mobile phones and therefore losing its market share. The benefits of understanding the relevant environment of business are:
i) Identification of opportunities to get first mover advantage: By keeping in touch with the changes in the external environment, an enterprise can identify opportunities and find strategies to capitalise on the opportunities at the earliest. For example, Volvo, the Swedish brand, has 74% share in the luxury bus segment as it had entered India earlier.
ii) Formulation of strategies and policies: It helps in identifying threats and opportunities in the market. These can serve as the basis of formulation of strategies to counter threats and capitalise on opportunities in the market.
iii) Tapping useful resources: If the company has a thorough knowledge of the external environment, it can tap raw materials, technology and even financial resources from the market at economical prices, at the right time.
iv) Better performance: Proper understanding of the various elements of the external environment is necessary to take timely action to deal with threats and avail opportunities for the purpose of improvement in the performance of the firm.
v) Sensitisation of entrepreneurs to cope up with rapid changes: A keen watch on the trends in the environment would help sensitise the entrepreneur to changing technology, competition, government policies and changing needs of the customers. For example, trends in clothing.
vi) Image building: If a company is sensitive to the external environment, it will come out with new products and services to meet the requirements of the customers. This would build the image or reputation of the firm in the eyes of the general public. For example, call–radio taxis with additional features like GPS systems, online booking etc.