Read and download the CBSE Class 11 Biology VBQs Neural Control and Coordination. Designed for the 2025-26 academic year, these Value Based Questions (VBQs) are important for Class 11 Biology students to understand moral reasoning and life skills. Our expert teachers have created these chapter-wise resources to align with the latest CBSE, NCERT, and KVS examination patterns.
VBQ for Class 11 Biology Chapter 18 Neural Control and Coordination
For Class 11 students, Value Based Questions for Chapter 18 Neural Control and Coordination help to apply textbook concepts to real-world application. These competency-based questions with detailed answers help in scoring high marks in Class 11 while building a strong ethical foundation.
Chapter 18 Neural Control and Coordination Class 11 Biology VBQ Questions with Answers
Question. Which of the following pair is incorrect?
Cerebral lobe Function
(a) Parietal lobe – Integrating sensory input
(b) Occipital lobe – Interpretation of shape and colour
(c) Frontal lobe – Judgement and decision nmaking
(d) Temporal lobe – Controls intellectual ability
Answer. D
Question. Which one of the following is an inhibitory neurotransmitter?
(a) GABA
(b) Nor adrenaline
(c) Epinephrine
(d) Acetylcholine
Answer. A
Question. Five events in the transmission of nerve impulse across the synapse are given.
A. Opening of specific ion channels allows the entry of ions, a new action potential is generated in the post-synaptic neuron.
B. Neurotransmitter binds to the receptor on post synaptic membrane.
C. Synaptic vesicle fuses with pre-synaptic membrane, neurotransmitter releases into synaptic cleft.
D. Depolarisation of pre-synaptic membrane.
E. Arrival of action potential at axon terminal.
What is the sequence of events in transmission of nerve impulse?
(a) E → D → C → B → A
(b) A → B → C → D → E
(c) A → B → D → C → E
(d) E → D → C → A → B
Answer. A
Question. Transmission of nerve impulse, across a synapse, is accomplished by
(a) release of phosphorus ion only
(b) movement of Na+ and K+
(c) release of neurotransmitters
(d) movement of water level.
Answer. C
Question. Motor end plate junction is present between
(a) neuron and muscle
(b) neuron and neuron
(c) muscle and muscle
(d) none of these.
Answer. A
Question. Read the following five statements (i) to (v) regarding left cerebral hemisphere and select the option that correctly states the true (T) and false (F) statements.
(i) It receives most modalities of sensory information from the right side of the body.
(ii) It is usually larger than the right cerebral hemisphere.
(iii) It is the dominant cerebral hemisphere in most individuals.
(iv) It is connected to the right cerebral hemisphere by the corpus callosum.
(v) It contains the main areas for the understanding and production of speech in most individuals.
(i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v)
(a) T T F F F
(b) F T T F T
(c) T F T T T
(d) F F T T T
Answer. C
Question. Not a part of limbic lobe or limbic system of brain is
(a) amygdala
(b) hippocampus
(c) cerebellum
(d) inner parts of cerebrum.
Answer. C
Question. Opening that connects the IV ventricle of the brain to the outside is
(a) foramen of Monro
(b) foramen of Magendie
(c) foramen ovale
(d) foramen magnum.
Answer. B
Question. Choroid plexus is a network of
(a) capillaries
(b) medulla oblongata
(c) cerebellum
(d) spinal cord.
Answer. A
Question. Each spinal nerve in a mammal arises from the spinal cord by two roots, a dorsal and a ventral. Of these the ventral root is composed of
(a) somatic motor and visceral motor fibres
(b) somatic motor and visceral sensory fibres
(c) somatic sensory and visceral motor fibres
(d) somatic sensory and visceral sensory fibres.
Answer. A
Question. Brain depends on blood for the supply of
(a) oxygen and ATP
(b) oxygen and electrolytes
(c) oxygen and glucose
(d) ATP and glucose.
Answer. C
Question. Thermoregulatory centre in brain of man is
(a) pituitary
(b) diencephalon
(c) hypothalamus
(d) none of these.
Answer. C
Case II : Read the following passage and the given table and answer the questions from 44 to 48 given below.
Human brain protected by the skull is the central information processing organ of our body and acts as the command and control system.
Brain is divided into three major parts :
(i) Forebrain,
(ii) Midbrain and
(iii) Hindbrain.
Answer. C
Question. Which of the following functional areas of cerebrum are involved in memory and learning?
(a) A
(b) B
(c) C
(d) D
Answer. A
Question. A person is able to understand written or spoken words but unable to speak fluently.
Which area of brain is affected in this condition?
(a) Temporal lobe of cerebrum
(b) Frontal lobe of cerebrum
(c) Parietal lobes of cerebrum
(d) Occipital lobe of cerebrum.
Answer. B
Question. Which of the following is not a part of cell body of neuron?
(a) B
(b) C
(c) G
(d) A
Answer. C
Question. Part of brain that contains centres for breathing, swallowing, sneezing, blood pressure is
(a) A
(b) B
(c) C
(d) D
Answer. B
Question. Select the incorrect statement regarding D.
(a) It is the second largest part of human brain.
(b) It is sometimes called as emotional brain.
(c) All of the activities are involuntary.
(d) Both (b) and (d)
Answer. B
Assertion & Reasoning Based MCQs
For question numbers 49-58, two statements are given-one labelled Assertion and the other labelled Reason. Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given below.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false but reason is true.
Question. Assertion : Nerve impluse can be transmitted from dendrite of one neuron to the axon of the next neuron, across a synapse.
Reason : This happens because of the synaptic delay at each synapse.
Answer. C
Question. Assertion : Brain and spinal cord has a common covering.
Reason : Both the brain and spinal cord possess meninges.
Answer. A
Question. Assertion : Medulla contains centres which control respiration, cardiovascular reflexes and gastric secretions.
Reason : Medulla contains several neurosecretory cells which secrete hormones.
Answer. C
Question. Assertion : Nerve impulse is originated from threshold stimulus.
Reason : Threshold stimulus is the minimum strength of stimulus which is applied to the nerve fibre to stimulate it effectively.
Answer. B
Question. Assertion : Cerebrospinal fluid is present in the space between the pia and arachnoid maters.
Reason : It serves to maintain a constant pressure inside the cranium.
Answer. B
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question. Our reactions like aggressive behaviour, use of abusive words, restlessness, etc., are regulated by brain. Name the parts involved.
Answer. Inner parts of cerebral hemispheres and group of associated deep structures like amygdala, hippocampus and hypothalamus regulates reactions like aggressive behaviour, use of abusive words, restlessness etc.
Question. Where are the Nissl’s granules located?
Answer. Nissl’s granules are located in the cytoplasm of cell body and dendrites.
Question. State the functions of nervous system.
Answer. The functions of nervous system are as follows: (i) It gathers information from the outside of the body (called sensory function). (ii) It transmits the information to the processing area of the brain and spinal cord. (iii) It processes the information to determine the best response (called integrative function). (iv) It sends information to muscle glands and organs (effectors) so they can respond correctly (called motor function).
Question. Which type of impulse conduction occurs along a myelinated nerve fibre?
Answer. Saltatory conduction
Question. What do you mean by resting potential of a neuron?
Answer. The resting membrane potential of the axon of a neuron is the potential difference between inside and outside when the axon is “resting,” i.e., not actively conducting impulses.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question. How are neurons classified on the basis of number of axons and dendrites?
Answer. On the basis of number of axons and dendrites, neurons are classified as : (i) Non-polar neurons : Each neuron has several branched processes (projections). These neurons are rare in vertebrates but occur in cnidarians (coelenterates), e.g., Hydra. (ii) Unipolar neurons : The body has only one axon and is found usually in the embryonic stage. (iii) Pseudounipolar neurons : In this, a single process arises from the cyton and then divides into axon and dendrite. They are found in dorsal root ganglia of spinal nerves. (iv) Bipolar neurons : Each bipolar neuron has one axon and one dendrite and are present in the retina of eye. (v) Multipolar neurons : They have several dendrites and an axon. They are found in cerebral cortex.
Question. Draw a well labelled diagram of myelinated neuron.
Answer. Diagrammatic representation of myelinated neuron is as follows: (Img 196)
Question. Axons and dendrites are the two neurites of neuron. How do they differ from each other?
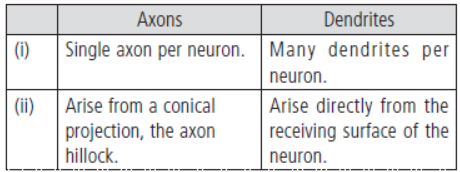
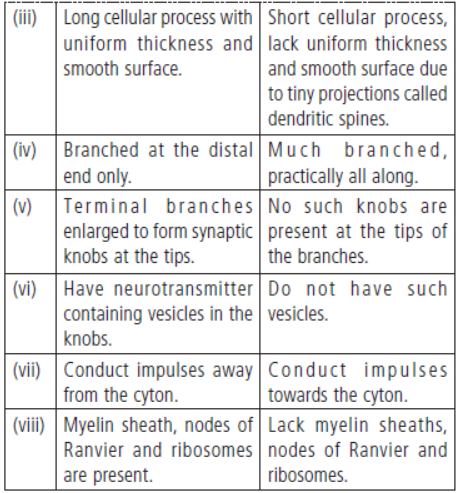
Answer. Axons and dendritFeisg .:c Satrnu cbtuer ed oiff fae nreeunrtoinated as follows:
Question. (a) Write down the differences between thalamus and hypothalamus.
(b) It is said that damage to medulla can cause death of a person. Justify this statement.
Answer. (a) Thalamus and hypothalamus can be differentiated as follows: (Table 197) (b) Several medullary centres (reflex centres) are present for controlling the functions of important organs, e.g., cardiac centre (heart), respiratory centre, vasomotor centre (for regulating diameter of blood vessels) and reflex centres (for swallowing, vomiting, peristalsis, secretions and activity of alimentary canal, salivation, coughing etc.). Therefore, damage of medulla can be fatal.
Question. Write a brief note on limbic system.
Answer. The limbic system is a group of brain structures that are involved in various emotions such as aggression, fear, pleasure and also in the formation of memory. It controls food habits necessary for survival of the individual. It also controls sex behaviour necessary for survival of the species. The limbic system affects the endocrine system and the autonomic nervous system. This system consists of several subcortical structures located around the thalamus such as: hippocampus involved in the formation of long-term memory; amygdala involved in aggression and fear; cingulate gyrus, fornicate gyrus; archicortex and hypothalamus that controls the autonomic nervous system and regulates blood pressure, heart rate, hunger, thirst, sexual arousal and the sleep/wake cycle.
Question. Briefly describe the spinal cord.
Answer. Spinal cord forms the posterior part of the CNS, running mid dorsally in the neural canal of the vertebral column. The spinal cord is formed of two types of nervous tissue : grey matter and white matter. The grey matter is internal, i.e., surrounds the central canal. It has the form of letter H in cross-section. The arms of H are called posterior and anterior grey columns. Portions of the grey matter present behind and in front of the central canal are called posterior and anterior grey commissures. At certain levels, the grey matter has lateral columns. The grey matter is composed of association neurons and cell bodies of motor neurons. The columns of the grey matter are continued into the roots of the spinal nerves. The white matter is outside the grey matter. It consists of bundles of medullated nerve fibres. Spinal cord conducts impulses to and from the brain and controls most of the reflex activities and provides a means of communication between spinal nerves and the brain.
Question. Briefly describe the main divisions of human nervous system?
Answer. The human nervous system consists of two sub-systems: The central nervous system (CNS) that consists of brain and spinal cord and the peripheral nervous system (PNS) which comprises of nerve pathways of the body outside brain and spinal cord. Peripheral nervous system is further divided into two main parts: (i) Voluntary or somatic nervous system is under voluntary control of brain that consists of the nerves supplying the skeletal muscles. (ii) Visceral or autonomic nervous system controls and coordinates those organs which are under involuntary control. This system is further divided into two—sympathetic nervous system (SNS), which has mainly excitatory effects on the body and parasympathetic nervous system, which acts antagonistically to the SNS and has mainly calming influences.
Question. What are the differences between myelinated and non-myelinated axons?
Answer. The differences between myelinated and non-myelinated axons are as follows :
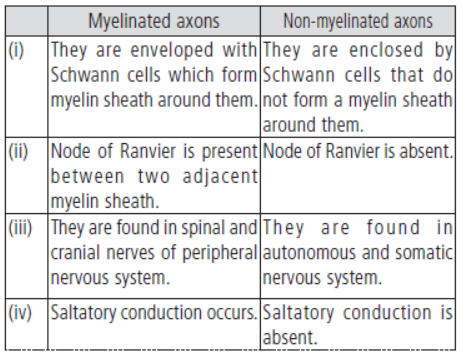
Long Answer Type Questions
Question. Briefly describe the structure of human brain.
Answer. Brain acts as control and command system of the body. It is protected by skull and is covered by three meninges. It is divisible into three main regions: forebrain, midbrain and hindbrain. (i) Forebrain consists of three regions: (a) Olfactory lobes are a pair of very small, solid club-shaped bodies which are widely separated from each other. They are fully covered by cerebral hemispheres. (b) Cerebrum is the largest and most complex of all the parts of human brain. A deep cleft divides the cerebrum into right and left cerebral hemispheres, connected by myelinated fibres, the corpus callosum. (c) Diencephalon encloses a slit-like cavity, the third ventricle. The thin roof of this cavity is known as the epithalamus, the thick right and left sides as the thalami and floor as the hypothalamus. (ii) Midbrain is located between thalamus/hypothalamus of forebrain and pons of hindbrain. Its upper surface has two pairs of rounded protrusious called corpora quadrigemina and two bundles of fibres called crura cerebri. (iii) Hindbrain consists of three regions : (a) Cerebellum is the second largest part of the human brain. It consists of two lateral cerebellar hemispheres and central worm-shaped part, the vermis. It has its grey matter on the outside, comprising three layers of cells and fibres. It also has Golgi cells, basket cells and granule cells. (b) Pons varolii is an oval mass lying above the medulla oblongata. It consists mainly of nerve fibres which interconnect different regions of the brain. (c) Medulla oblongata extends from the pons varolii above and is continuous with the spinal cord below. The mid brain, pons varolii and medulla oblongata are collectively called brain stem.
| CBSE Class 11 Biology VBQs The Living World |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology VBQs Biological Classification |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology VBQs Plant Kingdom |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology VBQs Animal Kingdom |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology VBQs Morphology Of Flowering Plants |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology VBQs Structural Organisation In Animals |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology VBQs Cell And Its Structure |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology VBQs Biomolecule |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology VBQs Cell Cycle |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology VBQs Photosynthesis In Higher Plants |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology VBQs Respiration in Plants |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology VBQs Plant Growth And Development |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology VBQs Body Fluids and Circulation |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology VBQs Excretory Products And Their Elimination |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology VBQs Locomotion And Movement |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology VBQs Neural Control and Coordination |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology VBQs Chemical Coordination and Integration |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology VBQs Mineral Nutrition |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology VBQs Transport In Plants |
Important Practice Resources for Class 11 Biology
VBQs for Chapter 18 Neural Control and Coordination Class 11 Biology
We hope students liked the above VBQs for Chapter 18 Neural Control and Coordination designed as per the latest syllabus for Class 11 Biology released by CBSE. Students of Class 11 should download the Value Based Questions and Answers in Pdf format and practice the questions and solutions given in above Class 11 Biology VBQs Questions on daily basis. All latest VBQs with answers have been developed for Biology by referring to the most important and regularly asked topics which the students should learn and practice to get better score in school tests and examinations. Expert teachers of studiestoday have referred to NCERT book for Class 11 Biology to develop the Biology Class 11 VBQs. After solving the questions given in the VBQs which have been developed as per latest course books also refer to the NCERT solutions for Class 11 Biology designed by our teachers. We have also provided a lot of other VBQs for Class 11 Biology which you can use to further make yourself better in Biology.
You can download the CBSE VBQs for Class 11 Biology Chapter 18 Neural Control and Coordination for latest session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the VBQs issued by CBSE for Chapter 18 Neural Control and Coordination Class 11 Biology have been made available here for latest academic session
There is no charge for the VBQs and their answers for Class 11 CBSE Biology Chapter 18 Neural Control and Coordination you can download everything free
Regular revision of VBQs given on studiestoday for Class 11 subject Biology Chapter 18 Neural Control and Coordination can help you to score better marks in exams
Value Based Questions (VBQs) for Class 11 Biology Chapter 18 Neural Control and Coordination help to test the ability of students to apply learnings to various situations in life.

