National Income and Related Aggregates Study notes
NATIONAL INCOME ACCOUNTING
In our modem economic setting the flow of production arises out of production of commodities - goods and services by millions of enterprises large and small. These enterprises range from giant corporations to single entrepreneur enterprises. Each producer of commodities intends to sell her output. The consumer may, in turn, be an individual or an enterprise and the good or service purchased might be for final use or for use in further production.
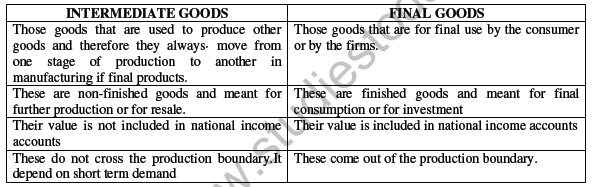
INTERMEDIATE AND FINAL GOODS
When the good or service is purchased for further production, it is known as an intermediate good. These are transformed through another productive process into final goods which is sold to for final use. Such an item that will not undergo any further transformation is called a final good.
Distinction between Intermediate and Final goods
Final goods can be further classified according to their use as consumer goods and capital goods.Consumer Goods: Goods like food and clothing, and services like recreation that are consumed when purchased by their ultimate consumers are called consumption goods or consumer goods. (This also includes services). These can be further identified according to their life time of use (Durability) as:
• Consumer Durables (Long time period of repeated use)
• Consumer Non-durables (Short time period of use OR single use)
• Consumer Services (Produced and consumed at same period of time)
Capital Goods: Goods that are of durable character like tools, implements and machines are used in the production process. These are also final goods but these are not ultimately consumed. These goods are capital good or a crucial factor of production in which an enterprise invests. A part of final output of capital goods constitutes Gross investment in an economy. These may be machines, tools and implements; buildings, office spaces, storehouses or infrastructure like roads, bridges, airports, etc.
These capital goods gradually undergo wear and tear (Depreciation OR consumption of Fixed Capital) and thus are repaired or gradually replaced over time. The stock of capital that an economy possesses is thus preserved, maintained and renewed partially or wholly over time. Depreciation does not take into account unexpected or sudden destruction or disuse of capital as can happen with accidents, natural calamities or other such extraneous circumstances
Distinction between Capital Loss and Consumption of Fixed Capital
All capital goods produced in a year do not constitute an addition to the capital stock already existing. New addition to capital stock in an economy is measured by net investment or new capital formation, which is expressed as:
Net Investment = Gross investment –Depreciation
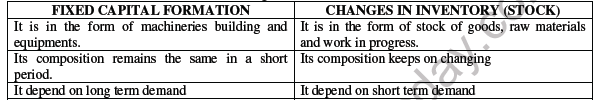
CONCEPT OF STOCKS AND FLOWS
Income, or output, or profits are concepts that are measured only when a time period is specified. These are called flows because they occur in a period of time. Flows are defined over a period of time.
Capital goods or consumer durables once produced do not wear out or get consumed in a time period. These continue to serve through different cycles of production. There can be addition or deduction made from these goods. These are called stocks. Stocks are defined at a particular point of time.
Distinction between Flows and Stocks
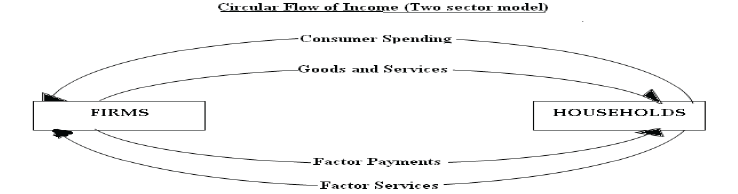
CIRCULAR FLOW OF INCOME
Total output of final goods and services produced in an economy in a year has two different parts. The households in the economy make up its workforce, which supply their factor services of Land, Labour, Capital and Enterprise to firms. Firms combine their stock of capital goods, tools, machines, infrastructure etc. to produce goods and services.
Households receive factor payments (Rent, Wages, Interest and Profits) in return to their supply of factor services. The same factor income is used to buy the goods and services produced by the firms. This is called a circular flow of income.
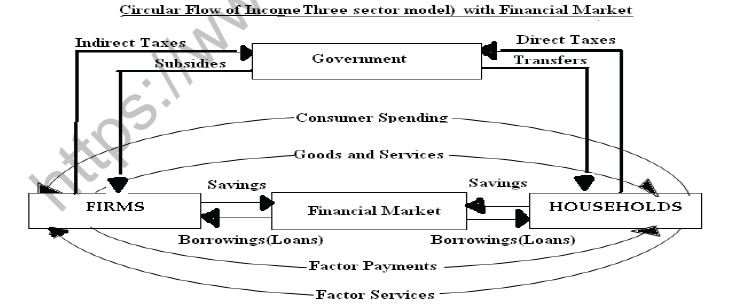
Both firms are households also save a part of their income in the financial market. At the same time the financial market uses these savings to extend loans as borrowings to both households and firms. Savings is considered as a leakage as money saved come out of the circular flow. Loans and borrowings are considered as Injections into the circular flow of income. The role of the financial market is to facilitate savings and borrowings.
Circular Flow of Income (Three Sector Model)
The role of the government in the circular flow is to collect direct taxes from households and indirect taxes from firms. Government also provides subsidies to firms and transfer payments to households.
Please click on below link to download CBSE Class 12 Economics National Income Accounting Worksheet Set E

