1 Marks Questions:
1. Initially the number of nuclei of a radioactive substance are 100. At t=1s these numbers become 80. Find the number of nuclei undecayed at t=2s.
2. Draw a graph of rate of formation of ‘Y’ against time ‘t’ when a radioactive nucleus ‘X’ decays to a stable nucleus ‘Y’?
3. A particle mass ‘m’ is projected from ground with velocity ‘u’ making angle ‘θ’ with the horizontal what will be the de-Broglie wave length of the particle at the highest point?
4. The difference between nth and (n + 1)th Bohr’s radius of hydrogen atom is equal to (n — 1)th Bohr’s radius. What is the value of n?
5. In the following nuclear fission reaction, N is the number of neutrons released in the fission of one 92U235
U235 + 0n1 → 38Sr94 + 54Xe140 + N
What is N here?
6. Some scientists have predicted that a global nuclear war on earth would be followed ‘nuclear winter’. What would cause ‘nuclear winter’?
7. The electron in the hydrogen atom passes from the n = 4 energy level to the n = 1 level. What is the maximum number of photons that can he emitted, and minimum number?
8. An electron is accelerated through a potential difference of 220 V.What is its energy in electron volts.
9. What is the Bohr’s frequency condition?
10. The mass number of He is 4 and that of sulphur is 32 .By what factor the radius of sulphur nucleus is larger than that of helium ?
2 Marks Questions:
11. A radioactive sample has 20 times of safe activity limit. After how many half lives will the radioactive sample be safe?
12. What is the angular momentum of the given wave function shown below, which is for an electron in a hydrogen atom.
13. The binding energy of an electron in the ground state of He is equal to 24.6 eV. What is the energy required to remove both the electrons?
14. For a hydrogen-like atom, if electrons move from lower energy level to higher energy levels, then what will happen to its KE and PE ?
15. Obtain Bohr’s quantization condition of angular momentum on the basis of wave picture of electron.
3 marks question:
16. In the fusion reaction 1H2 + 1H2 2He3 + 0n1, the masses of deuteron, helium and neutron expressed in amu are 2.015, 3.017 and 1.009 respectively. If 1 kg deuterium undergoes complete fusion, find the amount of total energy released. 1amu = 931.5 MeV/c2
17. 19K40 isotope of potassium has a half-life of l.4 x109 yr and decays to form stable argon, 18 Ar 40. A sample of rock has been taken which contains both potassium and argon in the ratio 1 :7, i.e.
no. of K40 atoms = 1/7
no. of Ar 40 atoms
Assuming that when rock is formed no Ar 40was present in the sample and none has escaped subsequently. Determine the age of rock.
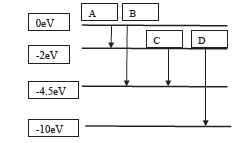
18. The energy levels of an atom are as shown below. Which one of the transitions will result in the emission of a photon of wavelength 275
nm?
19. How are protons, which are positively charged, held together inside a nucleus? Draw a graph between potential energy of a pair of nucleons as a function of their separation.
20. A neutron strikes a 5B10nucleus with the subsequent emission of an alpha particle. Write the Corresponding nuclear reaction. Find the atomic number, mass number and the chemical name of the remaining nucleus.
ANSWER
1 Marks Questions:
(1) 64
(2) expo. Graph
(3) h/mu cosθ
h
(4)We know ,rn α n2
So (n+1)2 -n2 =(n-1)2 →n=4
(5)
(6)
(7)
(8) 220eV \
(9) Elower-Ehigher hν = E − E
(10) 2
2 Marks Questions:
(11)The safe activity is present activity/20 since R0/25<R0/20<R0/20 so sample safe between some time lying between4th and 5th halve lives. Hence answer 5th halve lives
(12) If we trace a circle going around the center, we run into a series of eight complete Wavelengths. Its angular momentum is 8 h/2π
(13) To remove Ist electron Energy required is 24.6 eV , after removing it became He+ like Hydrogen atom whose B.E.is -4x13.6eV=-54.4eV.hence to remove both electron required energy=79eV
(14)For Hydrogen like atom, TE=-Ze2/4Πε0.2r, KE=+Ze2/8Πε0r, PE=-Ze2/4Πε0 hence KE decreases, PE(less negative)increases.
(15) When an electron confine to move on a line of length l with velocity ‘v’the de Broglie wavelength λ associated with electron is λ=h/p and λ=2l/n, when an electron revolves in a circular orbit of radius r; then 2l=2πr
p=nh/2πr or pxr=nh/2π
angular momentum (p×r) of electron is integral multiple of h/2π. This is Bohr’s quantization condition of angular momentum.
3 marks question:
(16) Δm = 2(2.015) − (3.017 +1.009) = 0.004amu Find energy released per deuteron 3.726/2MeV Then Number of deuterons in 1kg =N/2 hence energy released
=3.01x1026x1.863MeV=9.0×1013 J
(17) Age of the rock is 3 half lives of K nuclides. 4.2x109 yr.
(18)Energy of photon is =E=hc/λ 4.5eV clearly transition B will be the result.
(19)
(20)
ATOMIC NUCLEUS
1) what conclusions were drawn from the observation in which few alpha-particle were seen rebounding from gold foil?
2) which observation led to the conclusion in the α-particle scattering exp. That atom has vast empty space?
3) Compare the radii of two nuclei with mass number 1 and 27 respectively.
4) Two nuclei have mass numbers in the ratio 1:8.What is the ratio of their nuclear radii?
5) which have greater ionizing power:α-particles or β-particles?
6) The half life of a radioactive substance in 30 days. What is the time taken for ¾ of its original mass to disintegrate?
7) Why neutrons are considered as ideal particle for nuclear reactions?
8) Does the ratio of neutrons and protons in the nucleus increase, decreases or remain the same after the emission of ά – particles?
9) Why is the ionization power of ά – particle of greater than γ – rays?
10) A radio isotope of silver has a half life of 20 minutes. What fraction of the original mass would remain after one hour?
11) What changes takes place in the nucleus when a γ – rays is emitted?
12) Can a single nucleus emit ά – particle, β – particle and a γ – rays together?
13) Two nuclei have mass no. in the ratio 1:2. What is the ratio their nuclear densities?
14) Establish the relationship between half life of a radio- active substance and decay constant.
15) Explain how ά particle scattering experiment led to Rutherford to estimate the size of the nucleus.
16) The activity of a radio active material drops to 1-16th of its initial value in 30 days. Find its half life.
17) In a particular fission reaction, a U 235 nucleus captures a slow neutron. The fission products are 3 neutrons, a La 142 and fission products X y z .What is the value of Y and Z.
18) You are given two nuclides X b) Which one of the two is likely to be more stable? Give reason.
19) A certain radio active substance has a half life of 30 days. What is the disintegration constant? Find its average life.
20) Find the time required to decay 3/4th of a radioactive sample whose half life is 60 days.
21) Neon -23 decays in the following way
23Ne10 ---------------23Na11 + 0e-1 +γ
Find the minimum and maximum kinetic energy that the β-particle can have. The atomic masses of 23Ne10 and 23Na11 are 22.99454 and 22.98984 respectively.
22) The disintegration rate of a certain radioactive sample at any instant is 4750 disintegrations per minute. Five minutes later the rate becomes 2700 per minute. Calculate
a) Decay constant
b) Half-life of the sample
23) Explain with an example, whether neutron-proton ratio increases or decreases during beta decay.
24) The half life period of radioactive element A is the same as the mean half time of another radioactive element B.Initially both of them have the same number of atoms. The radioactive element B decays faster than A. Explain why?
25) Obtain the binding energy of a nitrogen nucleus from the following data mh=1.007834; mn=1.00867; mN=14.03074
Give your answer in MeV.
26) Write nuclear equations for
a) The α-decay of 226Ra88
b) The β- -decay of 32P15
c) The β+ decay of32P15
27) A neutron is absorbed by a 6Li3 nucleus with the subsequent emission of an alpha particle.
i) Write the corresponding nuclear reactions.
ii) Calculate the energy released in MeV, in this reaction.
Given mass 6Li3=6.0151264; mass (neutron) =1.00966544 Mass (alpha particle)=4.00260444 and mass(triton)=3.01000004
Extra Questions
1. Calculate the energy released in the following nuclear reaction.
3Li7 + 0n1 2He4 + 1H3
2. When a deutron of mass 2.0141amu is absorbed by a 3 Li 6 nucleus of mass 6.015amu, the nucleus splits into two a-particles each of mass 4.0026amu. Calculate energy carried by each α-particles.
4.0026amu. Calculate energy carried by each a-particles.
3. A nucleus 10 Na 23 undergoes β-decay to give 11 Na 23. Write down the nuclear reaction. Calculate KE of electron. Given mass of 10 Na 23 =22.994466amu, mass of 11 Na 23 = 2.989770amu.
4. A neutron is absorbed by 3 Li 6 nucleus with the subsequent emission of a a-particle. (i) Write the corresponding nuclear reaction.
(ii) Calculate the energy released. M 3Li6 = 6.015126amu, m(n) =1.0086654amu, mass of triton = 3.0100000amu.
5. The mass of the star is 5 * 1032 kg. It generates energy at the rate of 5 *1030 W. How long does it take to convert all Helium to carbon at this rate.
3 2 He4 → 6 C 12 + 7.27 MeV
6. Prove mathematically that the fraction N / N0 of a radioactive element left over after a time ‘t’ equals 1 / x where x = 2 t/T. T is half-life period.
7. The radioactive nuclei X and Y contain equal number of atoms. Their half-life periods are 1 H and 2 H respectively. Calculate the ratio of their activity after 2 Hrs.
8. How many disintegrations per sec will occur in one gm of 92 U 238, if its half-life period is 1.42 * 10 17 sec.
9. A radioactive sample contains 2.2mg of pure 6 C 11, having half-life period 1224seconds. Calculate (i) Number of active atoms
(ii) Activity when 5 μgm of sample is left.
10. The half-life period of 92 U 238 against a-decay is 4.5 * 109 years. What is the activity of 1g sample?
11. Obtain the amount of 27 Co 60 necessary to provide a radioactive source of 8 mC. The half-life period of Co60 is 5.3 years.
12. A 12.5 MeV a-particle approaching a gold nucleus is deflected back by 1800. How close does it approach the nucleus
15. Calculate half-life period and decay constant 1.0
16. The half-life period of radioactive sample is 5500 years. Its initial activity is found to be 15 decays per min per gram. In how much time would its activity reduces to 10 decays per min per gm? (Given loge3 = 1.0986 and loge2 0.693)
17. The decay constant for a given radioactive sample is 0.3465 days-1. What % of this sample gets decayed in a period of 4 days?
18. The nucleus 92U238is unstable against a-decay with a half-life of about 4.5x 109 years. Write down the equation of this decay and estimate the KE of emitted a-particle from the following data {m (92U238 = 238.05081 amu, m (2 He4 = 4.00260 amu, m (90Th234 = 234.04363 amu} (4.19 MeV)
19. How many α and β particles are emitted when 92U238 changes into 82Pb206.
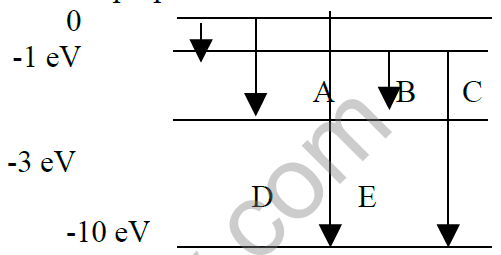
20. The energy level of an atom of element X is given below. Which one of the level transitions results in the emission of photon of wavelength 620 nm. Justify your answer with proper calculation
20. Calculate the longest and shortest wavelength of Lyman series. Given R = 10967700 m-1. (911.6 A0, 1215 A0)
21. The wavelength of second line of the Balmer series in hydrogen spectrum is 4861 A0. Calculate the wavelength of first line. (6562 A0)
22.Which state of the triply ionized beryllium atom (Be +3) has the same orbital radius as that of the ground state of hydrogen atom? {rn µ n2 /Z}Ans n = 2.
23.Which level of double ionized lithium (Li +2) has same energy as the ground state energy of hydrogen atom? Compare the orbital radius of two levels. {En µ Z2 / n2)
24. Calculate the frequency of photon, which can excite the electron to – 3.4 eV from – 13.6 eV. (2.47 × 1015 Hz)
25.Show that the shortest wavelength lines in Lyman, Balmer and Paschen series have their wavelength ratio 1: 4: 9.
26.The potential energy of the electron in ground state is –27 eV, what is its potential and kinetic energies?
27.Show that the wavelength of electromagnetic radiation is equal to the de Broglie wavelength of its photon.
28. A radioactive sample has N0 nuclei at t = 0. Its no. of undecayed nuclei get reduced to N0 /e at t = t. What does the term t stand for? Write in term of t the time interval ‘T’ in which half of original number of nuclei, of this radionucleide would have got decayed?
29. If the nucleus 26Fe56 splits into two nuclei of 13Al28. Would the energy be released or needed for this process to occur? Also calculate this energy.
Given m (26Fe56) = 55.93494 amu, m(13Al28 ) = 27.98191 amu.
30.Calculate the ratio of energies of photon due to transition of electron of hydrogen atom from (i) second permitted energy level to first level (ii) highest permitted energy level to second permitted level.
31. Prove that the instantaneous rate of change of activity of a radioactive substance is inversely proportional to the square of its half-life period.
32. The nucleus of an atom 92Y235 initially at rest decays by emitting an α-particle as per equation 92Y235 90X231 + 2He4 + energy. It is given that BE per nucleon of parent and the daughter nuclei are 7.8 MeV and 7.835 MeV and that of a-particle is 7.07 MeV / nucleon. Assuming the daughter nucleus to be formed in unexcited state and neglecting its share of in energy of the reaction, calculate the speed of emitted α-particle. Take mass of a-particle = 6.68 × 10-27 kg.
33. Four nuclei of an atom fuse together to form a heavier nucleus. If the process is accompanied by release of energy, which of the two parent or daughter nucleus have higher BE/nucleon?
34.The spectrum of a star in the visible and the ultraviolet region was observed and wave-length of some of the lines were identified were found to be 824 A0, 970 A0, 1120 A0, 2504 A0, 5173 A0, 6100 A0
Which of these lines cannot belong to hydrogen atom spectrum.(Given R = 1.03 × 107 m-1) and 1 / R = 970 A0. Support your answer with proper calculation.
35.Why a nucleus can eject electron (B particle) though it contain no electron?
36.Why nucleuses have mass less than the sum of masses of individual nucleons in them?
37.How wills the distance of closest approach changes: a) when the kinetic energy is of the projectile is doubled? B) when the velocity of projectile is halved.
38. The second member of Lyman series in hydrogen spectrum has wavelength 5400 Ao. Find the wavelength of first number.
39.What is the effect of temperature and pressure on the radioactivity?
40.What is the value of impact parameter of alpha particle scattered through an angle of 180o.
41.Draw the graph showing the distribution of electron’s emitted during beta decay.
1. In an atom, two electrons moves around the nucleus in circular orbit of radius R and 4R.Calculate the ratio of time taken to complete one revolution around the nucleus.
2. The spectrum of hydrogen atom has many lines although hydrogen atom contains only one electron.Why?
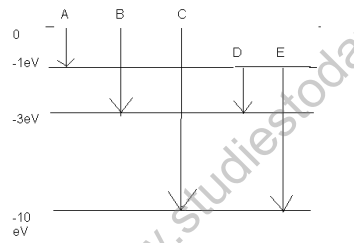
3. The energy level of an atom of an element ’X’ are shown in the diagram. A photon of wavelength 620 nm is emitted . This corresponds to which of the transition A,B,C,D or E.
4. Calculate the speed of electron revolving around the nucleus of a hydrogen atom in order that it may not be pulled into the nucleus by the electrostatic attraction ?
5. The spectrum of a star in the visible and the uv region was observed and the wavelength of some of the line that could be identified found to be : 824Å, 970 Å,1120 Å,2504 Å,5173 Å,6100 Å.Which of these lines cannot belong to hydrogen spectrum? R=1.03*107m-1 1/R=960 Å.Support the answer with suitable calculation.
6. Prove that Intanstaneous rate of change of change of the activity of a radioactive substance is inversely proportional to the square of its half life.
7. A radio active nuclei decays to form a stable nucleide. Its half life is 3 min.What fraction of its 1gm will remain radioactive after 9 minutes?
8. How much mass has to be converted to energy to produce electric power 500 MW for one hour?
9.A certain radioactive substance disintegrates for an interval of time equal to its mean life.
A)What fraction of element remains undecayed? B)What fraction of element has disintegrated?
10.How are β rays emitted from a nucleus when it does not contain any electrons?
11.Explain why heavy water is preferred as a moderator to ordinatory water in a nuclear reactor having uranium as a fuel?
12.The isotope 92U238 decays successively to form 90Th234 ,91Pa234 ,92U234 , 90Th230 , 88Ra226. What are the radiations emitted in these 5 steps?
13.Binding energy of Lithium(39.22 meV)is greater than binding energy of helium(27.22 meV).Even then Helium is more stable than lithium. Explain.
14.4 nuclei of an element fuse together to form a heavier nucleus .If the process is accompanied by release of energy ,which of the two –the parent or the daughter nuclei would have higher binding energy per nucleon.
15. Two different radioactive elements with half lives T1 & T2 have N1 & N2 atoms respectively present at a given instant .Determine the ratio of their activities at this instant.
16. A radioactive material is reduced to 1/16 of its original amount in 4 days .How much material should one begin with so that 4x10-3 of the material left after 6 days.
17. What do you understand by the term mirror isobars?
18.Show that the decay rate R of a sample of radio nuclei is related to the number of radioactive nuclei N at same instant by the expression R=Nxλ
19.How many α and β particles are emmited when 92U238 changes to 90th230
20.Draw a graph showing variation of P.E of a pair of nucleons as a function of their separation b.Indicate the reason in which nuclear force is
a)Attractive (b)Repulsive
21.Plot the distribution of K.E of β particles and state why the energy spectrum is continous?
22.You are given two nuclei 3X7 and 3Y4 .Explain giving reasons as to which one of the two nuclei is more stable?
23.If the nucleons bound in the nucleus are separated apart from each other ,the sum of their masses is greater than the mass of the nucleus.Where does this mass difference come from.Explain.
24.The wavelength of the first line of Lymann series for Hydrogen is identical to that of second line of Balmer series for some hydrogen like ion x.Calculate the energies of the first 4
levels of x.
25.At time t=0 activity of a radioactive substance is 1600 Bq. At t =8s activity remains 100 Bq . Find the activity at 2 seconds.
26. A radioactive nucleus undergoes a series of decay according to the scheme.
A→A1→A2→A3→A4 .If the mass number and atomic number of A are 180 and 72 respectively.What are these numbers A4
26. A gas of monoatomic hydrogen is bombarded with a stream of electrons that have been accelerated from rest through a potential difference of 12.75 V. Which spectral lines should be emitted?
27. An electron and anti particle, the positron, can form a bound system, called Positronium. What should be the ionization potential of positronium.
28. Estimate the energy needed to eject from a lead atom the electron with n = 1. What wavelength X ray would be required to do this ( Z = 82 ).
29. An alpha particle comes to with in 80 fm of gold nucleus . Assuming gold nucleus and the alpha particle are point charges, find the maximum repulsive force.
30. Show that if two ions of the same charge and velocity but of different mass pass through a uniform transverse magnetic field, the radii of the path are proportional to the masses. Find an expression for dm if dr is change in radius.
31. A nucleus X initially at rest, undergoes alpha decay according to the equation 92XA-----> Z Y 228 + Alpha particle. ( a ) find the values of A and Z. (b ) the alpha particle in the above process is found to move in a circular track of radius 1.1 X 102 m in a uniform field 3 X 10 3 T , find the energy during process and binding energy of parent nucleus ?
32. In experiment angles of scattering of alpha particle is 180. What is its impact parameter.
33. What will happen if electron revolving around the nucleus comes to rest.
34. By what factor must the mass number A change for the nuclear radius to double.
35. Initial amount of a radioactive substance is N0 . How much amount of the substance is left after 10 half lifes ?
36. Half life of a radioactive element A is same as mean life time of another radioactive element B. Initially both have same no of atoms. Explain why Beta decay faster than A.
37. Half life of radioactive substance A is two times the half life of another substance B.
Initially the no of nuclei of A and B are NA and NB . After three half lives of A number of nuclei of both are equal. What is ratio of NA and NB
38. 92U 238 changes to 85 At 210 by series of alpha , Beta decays. How many alpha , beta decay underwent?
39. Find the ratio between total acceleration of electron in singly ionized helium atom and hydrogen atom when both are in ground state.
40. The shortest wavelength of Brackett series of a hydrogen atom is the same as the shortest wavelength of Balmer series of hydrogen . Find the atomic no?
41. Find the maximum angular velocity of a electron of hydrogen atom in stationary orbit?
42. Find the ratio of maximum wavelength of Lymann series in hydrogen spectrum to the maximum wavelength in Paschen Series?
43. A electron and photon have same wavelength . If P is the momentum and E is energy of photon . Find the ratio of P/E.
44. B.E. per nucleon of hydrogen and helium are 1.1 eV and 7 MeV. Find the energy released in the process?
45. Find the probability of survival of a radioactive nucleus for one mean life?
46. The ratio of molecular mass of two radio active substances is 3/2 and ratio of their decay constant is 4/3. Find the ratio of their initial activity per mole?
47. A freshly prepared radio active substance of half life 2 hours emits radiation of intensity which is 64 times the permissible safe level. Find the minimum time after which it would possible to work with this source safely.
48. A star can convert all He nuclei completely into oxygen nuclei. Find the energy released per oxygen nuclei?
49. A beam of electron is used in YDS experiment. The slit width is d. What happens to fringe width?
50. A nucleus disintegrates in to two nuclear parts which have their velocities in the ratio 2 : 1. Find the ratio of their sizes
51. When a uranium originally at rest decays by emitting alpha particle having speed u. Find the recoil speed of residual nucleus?
52. The activity of a radioactive sample diminishes from 1024 to 128 in 2 min. Find how much activity diminishes in 6 min.
53. The activity of a radioactive element decreased to 1/3 of the original activity I0 in a period of 9 years. What its activity after further lapse of 9 years?
54. Half life of two substances A and B are 20 min and 40 min. Initially the sample have equal no of nuclei. Find after 80 min the ratio of remaining no of A and B nucleii?

