BIOTECHNOLOGY
Q.1. Name the molecular diagnostic techniques that should be referred to any patient for early diagnosis.
Ans: 1) Recombinant DNA technology
2) Polymerisation chain reaction
3) ELISA
Q.2. Give the term for rDNA, PCR and ELISA have common value.
Ans: rDNA, PCR and ELISA are tools of molecular diagnosis.
Q.3. Give the term for replacing a defective mutant allele with a functional allele.
Ans: Gene Therapy
Q.4. Give the term for increasing the content of gene.
Ans: Gene amplification
5. What is the principle of ELISA?
Ans: To study the antigen – antibody interaction
Q.6. What is common in the recognition sequence of all the organisms and strains, which are recognized by restriction enzymes.
Ans: Palindromic nucleotide sequence
Q.7. Can you recall meiosis and indicate at what stage a recombinant DNA in made?
Ans: Pachytene of meiosis –I
Q.8. What is golden rice?
Ans: GM rice with Vit A
Q.9. Does your blood have proteases and nuclease? If so what is its function?
Ans: Formation of blood clot.
Q.10. Which enzyme is used to remove phosphate group from the 5’ end of a DNA molecule.
Ans: Alkaline phosphate
Q.11. Bioreactors are important aspect of Bio technology .How?
Ans: They are used for biological conversion of raw materials
Q.12. Name the Genetically engineered human insulin. How many amino acids are present in it?
Ans: Humulin. 51 amino acids.
Q.13. Out of 51 amino acids in insulin. How many amino acids present in chain A and B.
Ans: A-21
B-30
14. India is the world’s richest country in the Bio diversity .how is it affected.
Ans: Bio piracy
Q.15. What is the role of CDFD?
Ans: Centre in India responsible for DNA finger printing.
Q.16. Following are the molecular diagnostic techniques. Find the one which is not referred to any patient for early diagnosis.
(a) PCR (b)rDNA (c) ELISA (d) EFB
Ans: (d)
Q.17. What is the difference between these two plasmids?
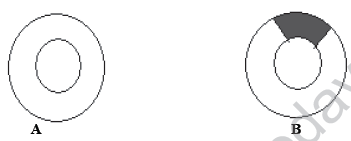
Ans: A is non recombinant and B is recombinant DNA.
Q.18. Eukaryotic organisms do not have restriction endonuclease. What is its role in prokaryotes?
Ans:: The prokaryotes have this as defence mechanism, to restrict the growth of bacteriophages.
Q.19. Thermostable DNA polymerase is needed in amplification? Why?
Ans: It remains active to denature the double stranded DNA.
PART – B (2 MARKS EACH)
Q.20. What is the role of Cry I Ac, Cry II Ab and Cry I Ab
Ans: Cry I Ab – controls corn borer Cry I Ac & Cry II Ab – control bollworms.
Q.21. What is the basis upon which the discipline of Biotechnology was founded by Boyer and Cohen?
Ans:: 1) Restriction endonuclease which cut the DNA at specific region.
2) Removal of plasmid from the cell and then reinserting them in other cell.
Q.22. The source of EcoR I restriction enzyme is E-coli RY 13.
1) Give the sticky end of this bacteria
2) Name the source of EcoR II
Ans:: 1) 5’ GAATTC 3’
3’ CTTAAG 5’
2) E-coli R245
Q.23. One of the easily manipulated plasmid used as a vector is pBR 322. What is the letter p, B, R and 322 signify?
Ans: p signifies plasmid →
B signifies Boliver → Scientist who has discovered
R signifies Rodriguer. →
322 signifies the order in which it is discovered.
Q.24. Name the recognition site and the antibiotic resistant gene found in pBR 322.
Recognition site Antibiotic resistant gene
Pvu 1, Pst 1 ________(1)___________
_(2)___ ,Sal 1 tetR
Ans: 1) ampR
2) BamH1
Q.25. Give one word for the following:-
1) RNAi
2) Preventing mRNA translation
3) Mobile genetic element
4) Sequence of base pairs that needs same on the 2 strands.
Ans:: 1) RNA interference
2) Silencing
3) Transposons
4) Palindromic sequence
26. Name the pallindromic DNA sequences and restriction enzymes.
(i) 5’__________________3’ EcoRI Restriction enzyme.
3’__________________5’
(ii) 5’ GGATCC 3’ ___________________________
3’ CCTAGG 5’
(iii) _____________ is acted upon by Sma I
______________
(iv) 5’ AGTACT 3’ _______________________
3’ TCATGA
Ans) (i) 5’ GAATTC 3’
3’ CTTAAG 5’
(ii) is acted upon by Bam HI
(iii) 5’ CCCGGG 3’
3’ GGGCCC 5’
(iv) is acted upon by Sca I
Q.27)

The electrophorosis apparatus is given.
(i) In which direction the DNA fragment resolve and why?
(ii) Where do you find the smallest and the largest fragment of DNA in the agarose gel?
Ans: (i) The DNA fragment moves towards anode, as the DNA is negatively charged.
(iii) smallest towards anode and largest towards cathode
Q.28. Complete the following table:--
Process Aim
(1) Preserves genetic information
Sexual reproduction (2)
(3) Leads to including and multiplication Of desired as well as undesired genes
Genetic engineering (4)
Ans.). 1. Asexual Reproduction
2. Permits the variation
3. Traditional hybridization
4. It includes cloning gene transfer and recombinant DNA formation.
Q.29) Give the technical term for following
(i) Molecular scissors.
(ii) Autonomous replicating circular DNA
(iii) First isolated restriction endonucleases
Ans) (i) Restriction endonuclease
(ii) Plasmids
(iii) Hind II
Q.30). Three steps to produce genetically modified organisms are
(i)Identification of DNA with _____________ (1) ______________
(ii)Introduction of identified DNA to _______ (2) _____________
(iii)Maintenance of DNA in host and transfer to _______(3)_________
Ans) (1) Desirable traits
(2) Host
(3) Its progeny
Q.31). Name the following:-
(i) 5’- GAATTC- 3’
3’- CTTAAG- 5’ -------------------
(iv) 5’------------------------3’
3’-----5’
___________?
Ans) (i) Pallindromic sequence.
(ii) Sticky/ Adhering ends.
(iii) Ori—origin of replication
(iv) Annealing of primers
Q.32. Name the enzyme involved in the following process:--
(i) Inspecting the DNA length for pallindromic nucleotide sequence
(ii) Joining of DNA fragments
(iii)Breaking of cell to release DNA and other macromolecules
(iv) Repeated DNA fragments.
Ans) (i) Restriction endonucleases
(ii) DNA ligases.
(iii) Lysozyme, cellulases
(iv) DNA/ Taq polymerase.
Q.33) Karl Ereky and Paul Berg are related to Biotechnology. Find their contribution.
Ans: 1] Karl Ereky – introduced the term Biotechnology.
2] Paul Berg – father of Genetic Engineering
Q.34) Name the following
1] Drug that was produced from slaughtered animals but now produced by using Biotechnology.
2] Technique used to detect the presence of virus in human.
Ans: 1] Insulin
2] ELISA
Q.35) Differentiate ‘Cry’ and ‘cry’
Ans: Cry stands for toxins produced by B.thuringiensis, cry for the gene that code for the synthesis.
Q.36) Give the term for (a) the DNA formed by joining together DNA from two different organisms and (b) the DNA obtained from an RNA template using the enzyme reverse transcriptase.
Ans: (a) rDNA and (b) cDNA
Q.37) What are the functions of enzymes isolated by Stewart Linn and Werner Arber?
Ans:- Restrict the growth of bacteriophage. One modifies enzyme added methyl group to the DNA and other cut DNA into segments.
Q.38) What is the difference between stirred tank bioreactor and sparged stirred tank bioreactor? What is its advantage?
Ans:- Sterile air bubbles are sparged in stirred –tank bioreactor.
The surface area for oxygen transfer is increased.
Q.39) A functional ADA cDNA is introduced into lymphocyte during Gene therapy. But the patient needs periodic infusion? What is the permanent cure in such situation?
Ans:- If the gene isolated from marrow cells is introduced in cells in the early stage, it could be a permanent cure.
Q.40) Give the options to increase food production?
Ans:- Agro-chemical, organic and GM crop based agriculture.
Q.41) Why do we still search for other alternatives to increase food production?
Ans:- Agrochemicals cause pollution. Increase in the yield by conventional breeding is not possible.
PART – C (3 MARKS EACH)
Q.42. Explain the process of curd formation from milk?
Milk is incubated with curd
|
LAB grows in milk
|
{1} Production
|
Coagulation & digestion of milk protein
|
Improved nutritional quality by {2}
[I] Complete the flow chart
[ii] Expand the word LAB
[iii] What is the role of LAB in human body?
Ans: [I]{1} Lactic acid
{2}Increased vitamin B-12
[ii] Lactic acid bacteria
[iii] It checks the disease causing microbes
Q. 43. __a____DNA __b___DNA
Study the linking DNA fragments shown above.
i) Name ‘a’ DNA and ‘b’ DNA.
ii) Name the restriction enzyme that recognizes this palindrome.
iii) Name the enzyme that can link these two DNA fragments.
Ans) (i) a is host DNA and b is vector DNA
(ii) EcoRI
(iii) DNA ligase
Q.44) Which of the following is not a tool for constructing rDNA?
(i) Heat shock
(ii) microinjection
(iii) Biolistics
(iv) Disarmed pathogens
(v) Insertional inactivation
Q.45) Complete the basic steps to create GMO
(i)---------------------------with desired gene
(ii)--------------------------- into host
(iii) -------------------------into progeny
Ans) (i) Identification of DNA
(ii) Introduction of DNA
(iii) Transfer of DNA
Q.46) Write the matching word:--
A B
(i)Hind II Gel electrophorosis
(2)Separation of DNA fragments. At tetracycline resistance gene in vector pBR 322
(3) BamH I first restriction endonuclease
Ans) (i) first restriction endonuclease.
(ii) Gel electrophorosis.
(iii)At tetracycline resistance gene in vector pBR 322.
PART—D (5 MARKS EACH )
Q.47) Complete the steps for separation and isolation of DNA fragments .
(i) Cutting of DNA by ---------------------------
(ii) During --------------- DNA fragments move to----------------------
(iii) ----------------separate in matrix of ------------
(iv) --------fragments move -----------------where as large remains nearer.
(v) DNA fragments are stained with ------------------
(vi) Stained fragments are exposed to -----------------
(vii) Fragments are extruded from gel piece. This is known as -------------------.
Ans) (i) Restriction endonucleases
(ii) Electrophorosis, anode
(iii) DNA fragments, Agarose.
(iv) small DNA, farther
(i) Ethidium bromide
(ii) UV light
(iii) Elution
48) (i)Complete the labeling in the following PCR.
(i) Expand the word PCR.
(ii) Give the origin of ‘Taq’
(iii) Whyis heating done in the procedure?
Ans) (i) a. Denaturing
b. Annealing
c. Extension
d. Amplification
(ii) Polymerase Chain Reaction
(iii) Isolated from bacteria Thermus aquaticus
(iv) To denature and separate DNA
Q.49) Find out how to make orally active protein pharmaceutical. What is the major problem to be encountered?
Ans.: 1) The present and oral pharmaceutical preparation contains acid or base embedded in an oily matrix which is controlled at neutral pH.
2) It is coated by an enteric coating.
3) The enteric coating enables the ingredient to reach the small intestine.
4) The oily matrix avoid acidic or basic conditions
5) It can isolate moisture and oxygen so as to allow for greater absorption.
Q.50)Following are 3 lines of treatment of ADA deficiency disease
1] Bone marrow transplantation
2] Enzyme replacement theory
3] Gene therapy
Give advantages and drawbacks of each.
Q.51)) Study the given flow chart and answer
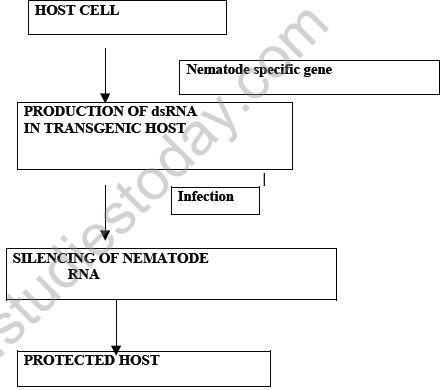
1] Name the defence mechanism used
2] In which plant has it been done?
3] Name the nematode infested.
Ans:1} RNAi
2} Tobacco
3} Meloidegyne incognitia
Q.52)
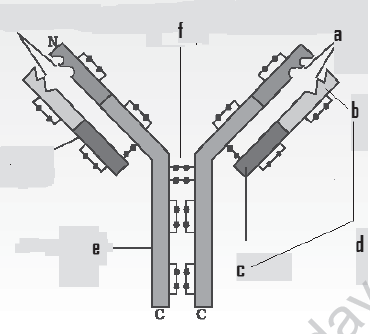
1} Name the parts labeled a to f
2} State the functions of a
3} Name the types of specific cells that produce antibodies.
Ans:1} a – antigen binding site
b – variable region of L chain
c – constant region of L chain
d – light polypeptide chain [L chain]
e – heavy polypeptide chain [H chain]
f – di sulfide [bond]
2} Each Y shaped molecule of antibody has 2 binding sites for antigen determinants [epitope present on the surface of pathogen and make them immobile or inactive.
3} Plasma cells [B – lymphocytes]
4} IgG , IgA, IgM, IgE, IgB
Q.53) Complete the following
1] The pathogens which are transformed to make them non virulent are called pathogens.
2] To isolate DNA from fungus cells, the later are treated with _________.
3] The culture system where in the used medium is drained out from one side , while fresh medium is added from the other is called _________.
Ans:1} Disarmed
2} Chitinase
3} Continuous culture system
54) Suggest a method to remove oil from seeds based on rDNA technology
Ans: 1. oil- one mol.glycerol+3 moles of fatty acids
2.By preventing the synthesis of either glycerol or lipase (catalyse the synthesis of oil)
3. Knockout the gene code for enzyme lipase or enzyme required for synthesis of glycerol.
55) How can the desired products formed after genetic engineering be produced on a commercial scale?
Ans: hints—1. downstream processing, preservatives, thorough clinical trials and quality control.

