Download CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Business Services Notes in PDF format. All Revision notes for Class 11 Business Studies have been designed as per the latest syllabus and updated chapters given in your textbook for Business Studies in Class 11. Our teachers have designed these concept notes for the benefit of Class 11 students. You should use these chapter wise notes for revision on daily basis. These study notes can also be used for learning each chapter and its important and difficult topics or revision just before your exams to help you get better scores in upcoming examinations, You can also use Printable notes for Class 11 Business Studies for faster revision of difficult topics and get higher rank. After reading these notes also refer to MCQ questions for Class 11 Business Studies given on studiestoday
Revision Notes for Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 4 Business Services
Class 11 Business Studies students should refer to the following concepts and notes for Chapter 4 Business Services in Class 11. These exam notes for Class 11 Business Studies will be very useful for upcoming class tests and examinations and help you to score good marks
Chapter 4 Business Services Notes Class 11 Business Studies
Business Services Class 11 Notes
Introduction
The chapter Business Services gives you a brief introduction to the characteristics of business services, the difference between services and goods, classification on types of business services, the concept of e-banking, identification and classification of types of insurance policies and the description of different types of warehouses. It has already been stated that commerce consists of trade and auxiliaries to trade. Auxiliaries or aids to trade refer to the activities incidental to the buying and selling of goods and services. These auxiliaries to trade are also known as business services or facilities. These services are essential and indispensable to the smooth flow of trade and industry. The examples of business services are Banking, insurance, transport, warehousing and communication.
Definition
Auxiliaries to trade are also known as business services. Service sector includes commercial firms engaged in banking, communication, transport, insurance and warehousing. Business cannot be even imagined in the absence of these services. All these services collectively constitute the Service Sector.
NATURE OF BUSINESS SERVICES :
1. Intangibility : Cannot be seen, touched or smelled. Just can only be felt, yet their benifits can be availed of e.g. Treatment by doctor.
2. Inconsistency : Different customers have different demands & expectation. e.g. Mobile services/Beauty parlour.
3. In Separability : Production and consumption are performed simultaneously e.g. ATM may replace clerk but presence of customer is a must.
4. Inventory Loss : Services cannot be stored for future use or performed earlier to be consumed at a later date. e.g. underutilised capacity of hotels and airlines during slack demand cannot be stored for future when there will be a peak demand.
5. Involvement : Participation of the customer in the service delivery is a must e.g. A cutomer can get the service modified according to specific requirement.
Type of Services :-
1. Social Services :- Provided voluntarily to achieve certain goals e.g. health care and education services provided by NGOs.
2. Personal Services :- Services which are experienced differently by different customers. e.g. tourism, restaurants etc.
3. Business Services :- Services used by business enterprises for the conduct of heir activities. e.g. Banking, Insurance, communication, warehousing and transportation.
Banks
Banks occupy an important position in the modern business world. No country can make commercial and industrial progress without a well organized banking system. Banks encourage the habit of saving among the public. They mobilize
small savings and channelize them into productive uses.
Meaning of Bank A bank is an institution which deals in money and credit. It collects deposits from the public and supplies credit, thereby facilitating exchange. It also performs many other function like credit creation, agency functions, general services etc Hence a Bank is an organization which accepts deposits, lends money and perform other agency functions.
Primary Functions :
1. Accepting Deposits Accepting deposits is the main function of commercial banks. Banks offer diffrent types of Bank accounts to suit the requirements and needs of different customers. Different types of Bank accounts are as follows :
- Fixed Deposit Account Money is deposited in the account for a fixed period. After expiry of specified period person can claim his money from the bank. Usually the rate of interest is maximum in this account. The longer the period of deposit, the higher will be the rate of interest on deposit.
- Current Deposit Account Current deposit Accounts are opened by businessman. The account holder can deposit and withdraw money whenever desired. As the deposit is repayable on demand, it is also known as demand deposit Withdrawals are always made by cheque. No interest is paid on current accounts. Rather charges are taken by bank for services rendered by it.
- Saving Deposit Account The aim of a saving account is to mobilise savingsof the public. A person can open this a/c by depositing a small sum of money. He can withdraw money from his account and make additional deposits at will. Account holder also gets interest on his deposit in this account though the rate of interest is lower than the rate of interest on fixed deposit account.
- Recurring Deposit Account The aim of recurring deposit is to encourage regular savings by the people. A depositer can deposit a fixed amount, say Rs. 100 every month for a fixed period. The amount together with interest is repaid on maturity. The interest rate on this account is higher than that on saving deposits.
- Multiple Option Deposit Account It is a type of saving Bank A/c in which deposit in excess of a particular limit gets automatically transferred into Fixed Deposit. On the other hand, in case adequate fund is not available in our saving Bank Account so as to honour a cheque that we have issued the required amount gets automatically transferred from fixed deposit to the saving bank account. Therefore, the account holder has twin benefits from this amount (i) he can earn more interest and (ii) It lowers the risk of dishonouring a cheque.
2. Lending Money With the help of money collected through various types of deposits, commercial banks lend finance to businessman, farmers, and others. The main ways of lending money are as follows :
- Term Loans These loans are provided by the banks to their customers for a fixed period to purchases Machinery, Truck, Scooter, House etc. The borrowers repay there loans in Monthly/Quarterly/Half Yearly/ Annual instalments.
- Bank Overdraft The customer who maintains a current account with the bank, takes permission from the bank to withdraw more money than deposited in his account. The extra amount withdrawn is called overdraft. This facility is available to trustworthy customers for a small period. This facility is usually given against the security of some assets or on the personal security of the customer. Interest is charged on the actual amount overdrawn by the customer.
- Cash Credit Under this arrangement, the bank advances cash loan up to a specified limit against current assets and other securities. The bank opens an account in the name of the borrower and allows him to withdraw the borrowed money from time to time subject to the sanctioned limit. Interest is charged on the amount actually withdraw.
- Discounting of Bill of Exchange Under this, a bank gives money to its customers on the security of a bill of exchange before the expiry of the bill in case a customers needs it. For this service bank charges discount for the remaining period of the bill.
Secondary Functions
The secondary functions of commercial banks are as under :
1. Ageny Functions
As an agent of its customers, a commercial bank provides the following services :
(a) Collecting bills of exchanges, promissory notes and cheques
(b) Collecting dividends, interest, rent etc.
(c) Buying and selling shares, debentures and other securities
(d) Payment of interest, insurance premium, etc
(e) Transferring funds from one branch to another and from one place to another
(f) Acting as an agent or representative while dealing with other banks and financial institutions.
A commercial bank performs the above functions on behalf of and as per the instructions of its customers.
2. General Utility Functions
Commercial banks also perform the following miscellaneous functions.
(a) Providing lockers for safe custody of jewellery and others valuables of customers.
(b) Giving references about the financial position of customers.
(c) Providing information to a customer about the credit worthiness of other customers.
(d) Supplying various
(e) Issuing letter of credit, pay orders, bank draft, credit cards, traveller s cheques to customers.
(f) Underwriting issues of shares and debentures.
(g) Providing foreign exchange to importers and travellers going abroad.
Bank Draft It is a financial instrument with the help of which money can be remitted from one place to another. Anyone can obtain a bank draft after depositing the amount in the bank. The bank issues a draft for the amount in its own branch at other places or other banks (only in case of tie up with those banks) on those places. The payee can present the draft on the drawee bank at his place and collect the money. Bank charges some commission for issuing a bank draft. **Banker s cheque or Pay Order It is almost like a bank draft. It refers to that bank draft which is payable within the town. In other words banks issue pay order for local purpose and issue bank draft for outstations.
ELECTRONIC BANKING SERVICES/E-BANKING
Using computers and internet in the functioning of the banks is called electronic banking. Because of these services the customers do not need to go to the bank every time he has to transact with bank. He can make transactions with the bank at any time and from any place. The chief electronic services are the following.
1. Electronic Fund Transfer Under it, a bank transfers wages and salaries directly from the company s account to the accounts of employees of the company. The other examples of EFTs are on line payment of electricity bill, water bill, insurance premium, house tax etc.
2. Automatic Teller Machines (ATMs) ATM is an automatic machine with the help of which money can be withdrawn or deposited by inserting the card and typing your personal Identity Number (PIN). This machine operates for all the 24 hours.
3. Debit Card A Debit Card is issued to a customers in lieu of his money deposited in the bank. The customers can make immediate payment of goods purchased or services obtained on the basis of his debit card provided the terminal facility is available with the seller.
4. Credit Card A bank issues a credit card to those of its customers who enjoy good reputation. This is a sort of overdraft facility. With the help of this card the holder can buy goods or obtain services upto a certain amount even without having sufficent deposit in their bank accounts.
5. Tele Banking Under this facilty, a customer can get information about the balance in his account or information about the latest transactions on the telephone.
6. Core Banking Solution/Centralised Banking Solution In this system a customer by opening a bank account in one branch (which has CBS facility) can operate the same account in all CBS branches of the same bank anywhere across the country. It is immaterial with which branch of the bank the customer deals with when he/she is a CBS branch customer.
7. National Electronic Fund Transfer : NEFT refers to a nation wide system that facilitate individuals, firms and companies to electronically transfer funds from any branch to any individual, firm or company having an account with any other bank branch in the country. NEFT settles transactions in batches. The settlement takes place at a particular point of time for example, NEFT settlement takes place 6 times a day during the week days (9.30am, 10.30 am, 12.00 noon, 1.00 pm, 3.00 pm & 4.00 pm) and 3 times during Saturday 9.30 am, 10.30 am and 12.00 noon) Any transaction initiated after a designated settlement time is settled on the next fixed settlement time. 8. Real Time Gross Settlement RTGS refers to a funds transfer system where transfer of funds takes place from one bank to another on a Real time and on Gross basis. Settlement in Real time means transactions are settled as soon as they are processed and are not subject to any waiting period. Gross settlement means the transaction is settled on one to one basis without bunching or netting with any other transaction. This is the fastest possible money transfer system through the banking channel. The RTGS service for customers is available from 9.00 am to 3.00 pm on week days and from 9.00 am to 12.00 noon on saturdays. The basic difference between RTGS and NEFT is that while RTGS transactions are processed continuously, NEFT settles transactions in batches. Meaning of insurance : Insurance is a form of contract under which one party (Insurer or Insurance Compnay) agrees in return of a consideration (Insurance premium) to pay an agreed sum of money to another party (Insured) to make good for a loss, damage or injury to something of value in which the insured has financial interest as a result of some uncertain event.
Banking Services
Bank is an institution that accepts deposits, withdrawal by cheques and makes loans and advances for the purpose of earning profits.
I. E-BANKING: E-banking means banking transactions carried out with the help of computer systems (i.e., that is banking over the internet).
1. Electronic Fund Transfer (EFT): Under this system, a bank transfers wages and salaries directly from the company’s account to the accounts of employees of the company.
2. Automatic Teller Machine (ATM): It refers to an electronic terminal that allows people with plastic card to perform simple banking transactions like withdrawal of cash 24x7 without
any help of human teller.
3. Debit Card: It refers to a plastic card that allows the bank to take money from the customer’s account and transfer it to a seller’s account.
4. Credit Card: It refers to a plastic card that allows the customer to buy now and payback the loaned amount to bank at a future date.
5. Online Banking: Under this system, when the customer gives instruction on his computer, the bank computer transfers money from/ to customer’s account to biller’s account.
· Insurance:
It is a contract where by in exchange of fixed consideration one party promises to pay a fixed amount either at happening of an event or at the expiry of certain period.
· Functions of Insurance
Principle of utmost faith: refers that no material or important facts should be concealed by both the parties of insurance contract.
Principle of Insurable Interest: There must be some pecuniary interest in the subject matter of the insurance contract.
Principle of Indemnity: Refers that the insured can get only the compensation against actual loss and he cannot make profit out of the insurance.
Principle of proximate cause: It refers to the direct cause and not the remote cause.
Principle of mitigation of loss: states that it is the duty of the insured to take reasonable steps to minimize the loss/damage to the insured property.
· Types of Insurance
Life Insurance: It is a contract under which the insurer, in consideration of a premium, undertakes to pay a fixed sum of money on the death of the insured or on the expiry of a specified period of time, which ever is earlier.
Fire insurance: it is a contract whereby the insurer undertakes to make good any loss/damage caused by fire during a specified period.
Marine Insurance: A marine insurance is an agreement where by the insurer undertakes to indemnify the insured loss against perils of the sea.
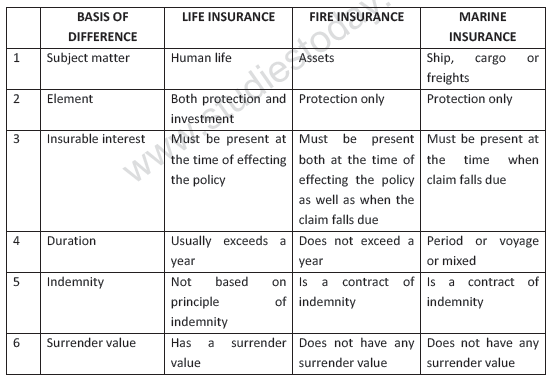
· Difference between life, fire and marine insurance
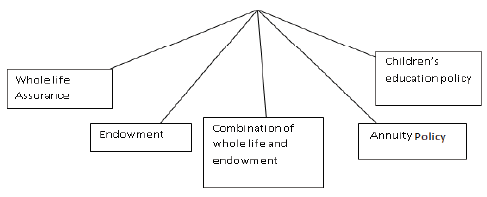
Types of Life Insurance Policies (Insurance Products)
Principles of Insurance : These principles are :
1. Utmost Good Faith : Insurance contracts are based upon mutual trust and confidence between the insurer and the insured. It is a condition of every insurance contract that both the parties insurer and the insured must disclose each fact and information related to insurance contract to each other.
2. Insurable Interest : It means some pecuniary interest in the subject matter of insurance contract. The insured must have insurable interest in the subject matter of insurance i.e., life or property insured, the insured will have to incur loss due to this damage and insured will be benefitted if full security is being provided. A businessman has insurable interest in his house, stock, his own life and that of his wife, children etc.
3. Indemnity Principle of indemnity applies to all contracts except the contract of life insurance because estimation regarding loss of life cannot be made. The objective of contract of insurance is to compensate to the insured for the actual loss he has incurred. These contracts provide security from loss and no profit can be made out of these contracts.
4. Proximate Cause : The insurance company will compensate for the loss incurred by the insured due to reasons mentioned in insurance policy. But if losses are incurred due to reasons not mentioned in insurance policy than principle of proximate cause or the nearest cause is followed.
5. Subrogation This principle applies to all insurance contracts which are contracts of indemnity. As per this principle, when any insurance company compensates the insured for loss of any of his property, then all rights related to that property automatically get transferred to insurance company.
6. Contribution According to this principle if a person has taken more than one insurance policy for the same risk then all the insurers will contribute the amount of loss in proportion to the amount assured by each of them and compensate him for the actual amount of loss because he has no right to recover more than the full amount of his actual loss.
7. Mitigation According to this principle the insured must take reasonable steps to minimise the loss or damage to the insured property otherwise the claim from the insurance company may be lost. (iMAGE 7)
Concept of Life Insurance : Under life insurance the amount of Insurance is paid on the maturity of policy or the death of policy holder whichever is earlier. If the policy holder survives till maturity he enjoys the amount of insurance. If he dies before maturity then the insurance claim helps in maintenance of his family. The insurance company insures the life of a person in exchange for a premium which may be paid in one lump sum or periodically say yearly, half yearly, quarterly or monthy.
Types of Life Insurance Policies.
1. Whole Life Police Under this policy the sum insured is not payable earlier than death of the insured. The sum then becomes payable to the heir of the deceased.
2. Endowment Life Assurance Policy Under this policy the insurer undertakes to pay the assured or his heirs or nominees a specified sum on the attainment of a particular age or on his death which every is earlier.
3. Joint Life Policy It involves the insurance of two or more lives simultaneously. The policy money is payable upon the death of any one of lives assured and the assured sum will be payable to the survivor or survivors.
4. Annuity Policy This policy is one under which amount is payable in monthly, quarterly, half yearly or annual instalments after the assured attains a certain age. This is useful to those who prefer a regular income after a certain age.
5. Children s Endowment Policy This policy is taken for the purpose of education of children or to meet marriage expenses. The insurer agrees to pay a certain sum when the children attain a certain age. Fire Insurance : It provides safety against loss from fire. If property of insured gets damaged due to fire the insured will receive the value of damaged property as compensation from insurance company. It no such event happens, insured will not receive anything. For such service insurance company charges premium depending upon the amount of loss insured.
Features
1. Utmost Good Faith
2. Contract of Indemnity
3. Insurable interest in the subject matter
4. Subject to the doctrine of causa premima - nearest cause.
5. It is a contract from year to year. It generally comes to an end at the expiry of the year and may be renewed. Marine Insurance : Marine insurance provides protection against loss during sea voyage. The businessmen can get their goods insured whereas the ship owner can get his ship insured by paying the premia fixed by the insurance company. The fundamental principles of marine insurance are the same as the general principles of insurance.
Other Insurance
Health Insurance : Health insurance has gained popularity these days. General Insurance companies provide special health insurance policies such as mediclaim for the general public. The insurance company charges a nominal premium every year and in return undertakes to provide up to stipulated amounts for the treatment of certain diseases such as heart problem, cancer, etc.
Communication services:
These are helpful to business for establishing links with outside world. The main service is postal and telecommunication.
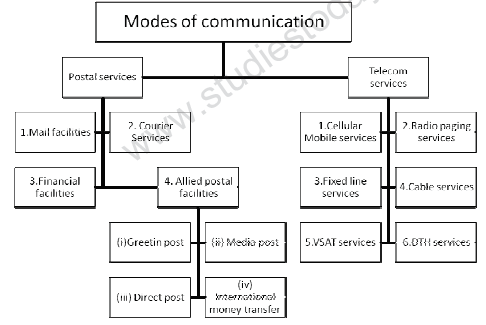
Communication is an important service that helps in establishing links between businessmen, Organisation, suppliers, customers etc. It educates people, widen their knowledge and broden their outlook. It overcomes the problem of distance between people, businessmen and institutions and thus helps in smooth running of trade, industrial and commercial activities. In this fast moving and competitive world it is essential to have advanced technology for quick exchange of information with the help of electronic media.
The main services can be classifed into postal and telecom. Postal Services Every business sends to outsiders and receives from outsiders several letters, market reports, parcell, money order etc. every day. All these services are provided by the post and telegraph offices scattered throughout the country. The postal department performs the following services.
1. Financial Services They provide postal banking facilities to the general public and mobilise their savings through the following saving schemes like public provident fund (PPF), Kisan Vikas Patra, National Saving Certificate, Recurring Deposit Scheme and Money Order facility.
2. Mail Services The mail services offered by post offices include transmission of messages through post cards, Inland letters, envelops etc. transmission of articles through parcel facility, registration facility and speed post to provide security of transmitted letters and articles and insurance facility to provide insurance cover for various risks in the course of transmission by post.
The various mail services all :
1. UPC (under postal certificate) When ordinary letters all posted the past office does not issue any receipt. However, if sender wants to have proof then a certificate can be obtained from the post office on payment of prescribed fee. This paper now serves as a evidence of posting the letters.
2. Registered Post Sometimes we want to ensure that our mail is difinitely delivered to the addressee otherwise it should come back to us. In such situations the post office offers registered post facility which serves as a proof that mail has been posted.
3. Parcel Transmission of articles from one place to another in the form of parcels is known as parcel post. Postal charges vary according to the weight of the parcels.
Allied Postal Services
1. Greetings Post Greetings can be sent through post offices to people at different places.
2. Media Post Corporates can advertise their brands through post cards, envelops etc.
3. Speed Post It allows speedy transmission of articles (within 24 hours) to people in specified cities.
4. e-bill post The post offices collect payment of bills on behalf of BSNL and other organisations.
5. Courier Services Letters, documents, parcels etc. can be sent through the courier service. It being a private service the employees work with more responsibility.
Telecom Services Today s global business world, the dream of doing business across the world, will remain a dream only in the absence of telecom services.
The various types of telecom services are
1. Cellular mobile services cordless mobile communication device including voice and non-voice messages, data services and PCO services.
2. Radio Paging Services means of transmitting information to persons even when they are mobile.
3. Fixed Line Services including voice and non-voice messages and data services to establish linkage for long distance traffic.
4. Cable services Linkages and switched services within a licensed area of operation to operate media services which are essentially one way entertainment related services.
5. VSAT Service (Very small Aperture Terminal) is a Satellite based communication service. It offers government and business agencies a highly flexible and reliable communication solution in both urban and rural areas.
6. DTH Services (Direct to Home) a Satellite based media services provided by cellular companies with the help of small dish antena and a set up box.
· Transportation:
It refers to the physical movement of goods from one place to another.
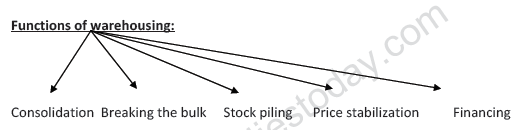
· Warehousing:
It refers to that activity under which goods are kept safely and systematically at a particular place.
Warehouse: It refers to the specially built building where the raw materials and finished goods are kept safely till their owner does need them.
· Types of Warehouses:
Gist of the Lesson:
Auxiliaries to trade are also known as business services.
Service sector include commercial firms engaged in banking, communication, transportation, insurance and warehousing.
Business can’t be even imagined in the absence of these services.
All the services collectively constitute the service sector.
Conclusion
We hope you liked the business services class 11 notes provided above. The notes have been prepared by teachers of Class 11 for the benefit of students. You will be able to understand all the important topics given in the chapter. You should read these revision notes for business services class 11 before your exams. This will help you to gain more marks.
Please click the link below to download pdf file for CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Business Services
| CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Nature And Purpose Of Business Notes |
| CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Forms Of Business Organisation Notes |
| CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Public Private And Global Enterprises Notes |
| CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Business Services Notes |
| CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Emerging Modes Of Business Notes |
| CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Social Responsibilities Of Business And Business Ethics Notes |
| CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Sources Of Business Finance Notes |
| CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Small Business Notes |
| CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Internal Trade Notes |
| CBSE Class 11 Business Studies International Business Notes |
CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 4 Business Services Notes
We hope you liked the above notes for topic Chapter 4 Business Services which has been designed as per the latest syllabus for Class 11 Business Studies released by CBSE. Students of Class 11 should download and practice the above notes for Class 11 Business Studies regularly. All revision notes have been designed for Business Studies by referring to the most important topics which the students should learn to get better marks in examinations. Our team of expert teachers have referred to the NCERT book for Class 11 Business Studies to design the Business Studies Class 11 notes. After reading the notes which have been developed as per the latest books also refer to the NCERT solutions for Class 11 Business Studies provided by our teachers. We have also provided a lot of MCQ questions for Class 11 Business Studies in the notes so that you can learn the concepts and also solve questions relating to the topics. We have also provided a lot of Worksheets for Class 11 Business Studies which you can use to further make yourself stronger in Business Studies.
You can download notes for Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 4 Business Services for latest academic session from StudiesToday.com
Yes, the notes issued for Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 4 Business Services have been made available here for latest CBSE session
There is no charge for the notes for CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 4 Business Services, you can download everything free of charge
www.studiestoday.com is the best website from which you can download latest notes for Chapter 4 Business Services Business Studies Class 11
Come to StudiesToday.com to get best quality topic wise notes for Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 4 Business Services

