Read and download free pdf of CBSE Class 11 Biology Neural Control and Coordination Assignments. Get printable school Assignments for Class 11 Biology. Class 11 students should practise questions and answers given here for Chapter 18 Neural Control And Coordination Biology in Class 11 which will help them to strengthen their understanding of all important topics. Students should also download free pdf of Printable Worksheets for Class 11 Biology prepared as per the latest books and syllabus issued by NCERT, CBSE, KVS and do problems daily to score better marks in tests and examinations
Assignment for Class 11 Biology Chapter 18 Neural Control And Coordination
Class 11 Biology students should refer to the following printable assignment in Pdf for Chapter 18 Neural Control And Coordination in Class 11. This test paper with questions and answers for Class 11 Biology will be very useful for exams and help you to score good marks
Chapter 18 Neural Control And Coordination Class 11 Biology Assignment
Important Questions for NCERT Class 11 Biology Neural Control and Coordination
Ques. In a man, abducens nerve is injured. Which one of the following functions will be affected?
(a) Movement of the eyeball
(b) Movement of the tongue
(c) Swallowing
(d) Movement of the neck
Answer: A
Question. Intercellular communication in multicellular organism occurs through
(a) digestive system only
(b) respiratory system only
(c) nervous system only
(d) both nervous and endocrine system.
Answer. D
Question. Nerve fibre gets depolarised when it acquires
(a) +ve charges on inner side
(b) +ve charges on outer side
(c) –ve charges on inner side
(d) Na+ and K+ from outside.
Answer. A
Question. Which of the following statement is correct about node of Ranvier of neuron?
(a) Neurilemma is discontinuous.
(b) Myelin sheath is discontinuous.
(c) Both neurilemma and myelin sheath are discontinuous.
(d) Covered by myelin sheath.
Answer. B
Question. Pre-synaptic membrane is part of
(a) dendron
(b) axon hillock
(c) telodendria
(d) soma.
Answer. C
Question. Column I lists the parts of the human brain and column II lists the functions. Match the two columns and select the correct option.
Column I Column II
A. Cerebrum p. Controls the pituitary
B. Cerebellum q. Controls vision and hearing
C. Hypothalamus r. Controls the rate of heart beat
D. Midbrain s. Seat of intelligence
t. Maintains body posture
(a) A-t; B-s; C-q; D-p
(b) A-s; B-t; C-q; D-p
(c) A-t; B-s; C-p; D-q
(d) A-s; B-t; C-p; D-q
Answer. D
Question. Four healthy people in their twenties got involved in injuries resulting in damage and death of few cells of the following. Which of the cells are least likely to be replaced by new cells?
(a) Osteocytes
(b) Malpighian layer of the skin
(c) Liver cells
(d) Neurons
Answer. D
Question. Which labelled part in the given diagram controls the process of breathing? (Img 185)
(a) A
(b) B
(c) C
(d) D
Answer. C
Question. Which part of neuron is highly branched and afferent?
(a) Axon
(b) Dendrite
(c) Cyton
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer. B
Question. Select the incorrect statement.
(a) The Nissl’s granules probably synthesise fats for the cell
(b) Ageing neuron contain a pigment lipofuscin
(c) Nissl’s granules are irregular masses of rough endoplasmic reticulum
(d) None of these
Answer. A
Question. By which nervous system, the blood is supplied into visceral organs?
(a) Sympathetic nervous system, voluntary
(b) Sympathetic nervous system, involuntary
(c) Parasympathetic nervous system, involuntary
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Answer. D
Question. The given diagram shows axon terminal. Select the option that correctly matches the steps in transmission of impulses (list i – vii) with the labellings (A – C) in diagram.
(i) Chemicals called neurotransmitters are released in the synaptic cleft through ion channels. (Img 185)
(ii) When an impulse arrives at the axon terminal, it stimulates the movement of synaptic vesicles.
(iii) Neurotransmitters are endocytosed into the neurons.
(iv) The ion channels close with the binding of neurotransmitters to their specific receptors vesicles.
(v) Synaptic vesicles move towards the membrane where they fuse with the plasma membrane.
(vi) Neurotransmitters are released in the synaptic cleft.
(vii) The released transmitters bind to their specific receptors on post-synaptic membrane.
A B C
(a) (ii) (iii) (i)
(b) (v) (vi) (iv)
(c) (ii) (vi) (vii)
(d) (v) (iii) (iv)
Answer. C
Question. Read the given statements and select the correct option.
I. The continuity between the pre-synaptic and post-synaptic neurons is provided by gap junctions in chemical synapses.
II. Release of calcium ions from pre-synaptic knob stimulates the release of neurotransmitter into synaptic cleft.
III. More energy is required for impulse conduction through myelinated neurons due to saltatory conduction.
IV. After transmission of impulse, neurotransmitteris hydrolysed by an enzyme present at synapse.
(a) I and II are correct but III and IV are incorrect.
(b) I and IV are correct but II and III are incorrect.
(c) I, II and III are correct but IV is incorrect.
(d) I, II and III are incorrect, but IV is correct.
Answer. D
Ques. Injury to vagus nerve in humans is not likely to affect
(a) tongue movements
(b) gastrointestinal movements
(c) pancreatic secretion
(d) cardiac movements.
Answer: A
Ques. Which cranial nerve has the highest number of branches?
(a) Vagus nerve
(b) Trigeminal nerve
(c) Facial nerve
(d) None of these
Answer: B
Ques. Sympathetic nervous system induces
(a) secretion of digestive juices
(b) heart beat
(c) secretion of saliva
(d) all of these.
Answer: B
Ques. The vagus nerve is the cranial nerve numbering
(a) 7
(b) 5
(c) 10
(d) 9.
Answer: C
Ques. By which nervous system and of what type, the blood is supplied into visceral organs?
(a) Both SNS and PNS, involuntary
(b) Para-sympathetic nervous system involuntary
(c) Sympathetic nervous system, involuntary
(d) Sympathetic nervous system, voluntary
Answer: A
Ques. The sympathetic nerves, in mammals, arise from
(a) sacral nerves
(b) 3rd, 7th, 9th and 10th cranial nerves
(c) thoraco-lumbar nerves
(d) cervical nerves.
Answer: C
Ques. Afferent nerve fibres carry impulses from
(a) effector organs to CNS
(b) receptors to CNS
(c) CNS to receptors
(d) CNS to muscles.
Answer: B
Ques. Vagus nerve is
(a) X
(b) IX
(c) VII
(d) V.
Answer: A
Ques. One function of parasympathetic nervous system is
(a) contraction of hair muscles
(b) stimulation of sweat glands
(c) acceleration of heart beat
(d) constriction of pupil.
Answer: D
Ques. Which of the following cranial nerves can regulate heart beat?
(a) X
(b) IX
(c) VIII
(d) VII
Answer: A
Ques. Nissl’s bodies are mainly composed of
(a) proteins and lipids
(b) DNA and RNA
(c) nucleic acids and SER
(d) free ribosomes and RER.
Answer: D
Ques. Myelin sheath is produced by
(a) astrocytes and Schwann cells
(b) oligodendrocytes and osteoclasts
(c) osteoclasts and astrocytes
(d) Schwann cells and oligodendrocytes.
Answer: D
Ques. Receptor sites for neurotransmitters are present on
(a) pre-synaptic membrane
(b) tips of axons
(c) post-synaptic membrane
(d) membranes of synaptic vesicles.
Answer: C
Ques. The most abundant intracellular cation is
(a) H+
(b) K+
(c) Na+
(d) Ca++.
Answer: B
Ques. When a neuron is in resting state i.e., not conducting any impulse, the axonal membrane is
(a) comparatively more permeable to Na+ ions and nearly impermeable to K+ ions
(b) equally permeable to both Na+ and K+ ions
(c) impermeable to both Na+ and K+ ions
(d) comparatively more permeable to K+ ions and nearly impermeable to Na+ ions.
Answer: D
Question. Compare the central nervous system (CNS) with peripheral nervous system (PNS).
Answer. Central Nervous system (CNS) comprises of brain and the spinal cord. It is the site of information processing and control. Peripheral nervous system (PNS) consists of neurons. Some peripheral neurons (called afferent neurons) collect information from the tissue/organs and transmit it to the CNS and other neurons transmit regulatory information from the CNS to the concerned tissue or organ.
Question. What is the difference between electrical transmission and chemical transmission?
Answer. Differences between electrical and chemical transmission are as follows : (Table 195)
Question. Fill in the blanks at (A), (B), (C) and (D). (Img 190)
Answer. (A) – Neurotransmitter
(B) – Specific receptors
(C) – Ion channels
(D) – Postsynaptic neuron
Question. Briefly describe the thirst centre located in human brain.
Answer. Hypothalamus is the thirst centre present in human brain. It is located in the forebrain. It links nervous system to endocrine system (via hypothalamus - hypophyseal axis) and
exercises a regulatory control on the functioning of endocrine glands by secreting neurohormones. It contains higher centres of autonomic nervous system controlling hunger, thirst, sleep, fatigue, emotions, satisfaction, anger, pleasure, etc. It also controls carbohydrates and fat metabolism, body temperature, blood pressure and water balance.
Question. If someone receives a blow on the back of neck, what would be the effect on the person’s CNS?
Answer. If someone receives a blow on the back of the neck, then his medulla oblongata would get hurt, as this is the place where it is located. The person might die as medulla controls respiration, cardiovascular reflexes and gastric secretions.
Question. What does nervous system of earthworm comprise of?
Answer. Earthworm has a nervous system consisting of well developed ventral nerve cord, paired segmental ganglia and segmental nerves.
Question. Name the following.
(a) The part of the human brain that is most developed.
(b) Part of our central nervous system that acts as a master clock.
(c) The scattered masses of grey matter.
(d) The additional space lying above the duramater.
Answer. (a) Cerebrum (cerebral hemispheres). (b) Pineal gland (c) Basal ganglia (d) Epidural space
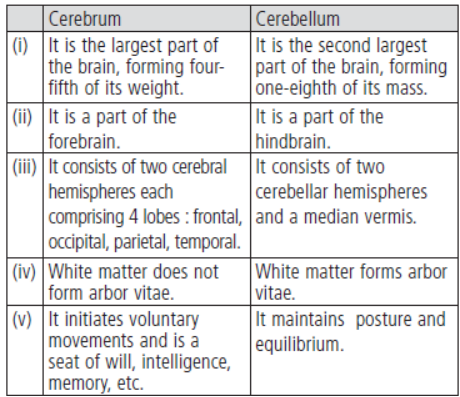
Question. Distinguish between cerebrum and cerebellum.
Answer. Cerebrum and cerebellum can be differentiated as follows:
Long Answer Type Questions
Question. Explain the detailed structure of a neuron with a suitable diagram.
Answer. A neuron (nerve cell) is the structural and functional unit of the neural system. Neurons with longer processes (projections) are the longest cells in the body. Fully formed neurons never divide and remain in interphase stage throughout life. Shortly after birth, new neurons do not develop. A neuron is a microscopic structure composed of three major parts, namely, cell body, dendrites and axon. (i) Cell body (Cyton or Soma) : Like a typical cell, it consists of cytoplasm, nucleus and cell membrane. It has abundant cytoplasm called neuroplasm and a relatively large spherical central nucleus with a distinct nucleolus. The cytoplasm has mitochondria, Golgi apparatus, rough endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, lysosomes, fat globules, pigment granules, neurofibrils, neurotubules and Nissl’s granules. Cyton is concerned with metabolic maintenance and growth. The processes of neurons are called neurites that are divided further into dendrites and axons. (ii) Dendrites are usually shorter, tapering and much branched processes that may be found here one to several. They conduct nerve impulse towards the cell body and are called afferent processes. (iii) Axon is a single, usually very long process of uniform thickness. The part of cyton from where the axon arises is called axon hillock. It is the most sensitive part of neuron. The axon contains neurofibrils and neurotubules but lacks Nissl’s granules, Golgi complex, ribosomes, pigment granules, fat globules, etc. The cell membrane of the axon is called axolemma and its cytoplasm is known as axoplasm. The axon ends in a group of branches, the terminal arborisations which when meet the dendrites of another neuron to form a synapse, form synaptic knobs or end plates. The synaptic knobs contain mitochondria and secretory vesicles. The part of the sarcolemma (muscle plasma membrane) that lies beneath the axon terminal/nerve endings, is called motor end plate. The axon conducts nerve impulses away from the cell body, therefore, called an efferent process. There are two types of nerve fibres namely myelinated and non-myelinated. The myelinated nerve fibres are enveloped with Schwann cells, which form a myelin sheath around the axon. The gaps between two adjacent myelin sheaths are called nodes of Ranvier. Non-myelinated nerve fibre is enclosed by a Schwann cell that does not form a myelin sheath around the axon. For labelled diagram of a neuron refer to answer 26.
Question. Explain the process of the transport and release of a neurotransmitter with the help of a labelled diagram showing a complete neuron, axon terminal and synapse.
Answer. Chemicals called neurotransmitters are involved in the transmission of impulses at chemical synapses. The axon terminals contain vesicles filled with these chemicals. When an impulse arrives at the axon terminal, it stimulates the movement of the synaptic vesicles towards the membrane where they fuse with the plasma membrane and release their neurotransmitters in the synaptic cleft. The released neurotransmitters bind to their specific receptors, present on the post-synaptic membrane. This binding opens ion channels allowing the entry of ions which can generate a new potential in the post-synaptic neuron. The given diagram shows neuron, axon terminal and synapse. (Img 199)
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Diversity in The Living World Assignments |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology The Living World Assignments |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Biological Classification Assignments |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Plant Kingdom Assignments |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Animal Kingdom Assignments |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Morphology of Flowering Plants Assignments |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Anatomy of Flowering Plants Assignments |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Structural Organisation in Animals Assignments |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Biomolecules Assignments |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Cell Cycle and Cell Division Assignments |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Photosynthesis in Higher Plants Assignments |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Respiration in Plants Assignments |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Plant Growth and Development Assignments |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Breathing and Exchange of Gases Assignments |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Body Fluids and Circulation Assignments |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Excretory Products and Their Elimination Assignments |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Locomotion and Movement Assignments |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Neural Control and Coordination Assignments |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Chemical Coordination and Integration Assignments |
| CBSE Class 11 Biology Revision Assignment |
CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 18 Neural Control And Coordination Assignment
We hope you liked the above assignment for Chapter 18 Neural Control And Coordination which has been designed as per the latest syllabus for Class 11 Biology released by CBSE. Students of Class 11 should download and practice the above Assignments for Class 11 Biology regularly. We have provided all types of questions like MCQs, short answer questions, objective questions and long answer questions in the Class 11 Biology practice sheet in Pdf. All questions have been designed for Biology by looking into the pattern of problems asked in previous year examinations. You can download all Revision notes for Class 11 Biology also absolutely free of cost. Lot of MCQ questions for Class 11 Biology have also been given in the worksheets and assignments for regular use. All study material for Class 11 Biology students have been given on studiestoday. We have also provided lot of Worksheets for Class 11 Biology which you can use to further make your self stronger in Biology.
What are benefits of doing Assignment for CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 18 Neural Control And Coordination?
a. Score higher marks: Regular practice of Biology Class 11 Assignments for chapter Chapter 18 Neural Control And Coordination will help to improve understanding and help in solving exam questions correctly.
b. As per CBSE pattern: All questions given above follow the latest Class 11 Biology Sample Papers so that students can prepare as per latest exam pattern.
c. Understand different question types: These assignments include MCQ Questions for Class 11 Biology with answers relating to Chapter 18 Neural Control And Coordination, short answers, long answers, and also case studies.
d. Improve time management: Daily solving questions from Chapter 18 Neural Control And Coordination within a set time will improve your speed and accuracy.
e. Boost confidence: Practicing multiple assignments and Class 11 Biology mock tests for Chapter 18 Neural Control And Coordination reduces exam stress.
How to Solve CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 18 Neural Control And Coordination Assignment effectively?
a. Start with Class 11 NCERT and syllabus topics: Always read the chapter carefully before attempting Assignment questions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 18 Neural Control And Coordination.
b. Solve without checking answers: You should first attempt the assignment questions on Chapter 18 Neural Control And Coordination yourself and then compare with provided solutions.
c. Use Class 11 worksheets and revision notes: Refer to NCERT Class 11 Biology worksheets, sample papers, and mock tests for extra practice.
d. Revise tricky topics: Focus on difficult concepts by solving Class 11 Biology MCQ Test.
e. Maintain notebook: Note down mistakes in Chapter 18 Neural Control And Coordination assignment and read them in Revision notes for Class 11 Biology
How to practice CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 18 Neural Control And Coordination Assignment for best results?
a. Solve assignments daily: Regular practice of Chapter 18 Neural Control And Coordination questions will strengthen problem solving skills.
b.Use Class 11 study materials: Combine NCERT book for Class 11 Biology, mock tests, sample papers, and worksheets to get a complete preparation experience.
c. Set a timer: Practicing Class 11 Biology Chapter 18 Neural Control And Coordination assignment under timed conditions improves speed and accuracy.
You can download free Pdf assignments for CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 18 Neural Control And Coordination from StudiesToday.com
All topics given in Chapter 18 Neural Control And Coordination Biology Class 11 Book for the current academic year have been covered in the given assignment
No, all Printable Assignments for Chapter 18 Neural Control And Coordination Class 11 Biology have been given for free and can be downloaded in Pdf format
Latest syllabus issued for current academic year by CBSE has been used to design assignments for Chapter 18 Neural Control And Coordination Class 11
Yes, we have provided detailed answers for all questions given in assignments for Chapter 18 Neural Control And Coordination Class 11 Biology

